Figure 6.
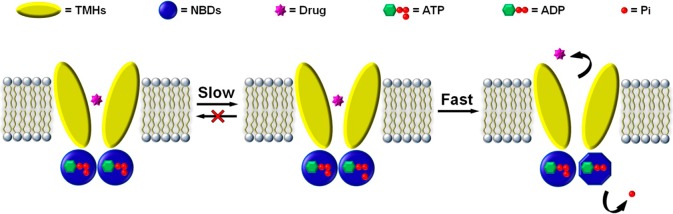
Schematized mechanism for conformational changes coupled to ATP hydrolysis in P-gp. A portion of the entire catalytic cycle is shown starting from the drug and nucleotide-bound state. After hydrolysis of one ATP, the conformational change and release of Pi are fast, preventing reformation of ATP or exchange of bound HPO42– with H2O. The conformational change is unlikely to include full dissociation of the NBD dimers but rather is fast with minor structural rearrangement. This conformational change is sufficient to ensure a high commitment to catalysis for ATP hydrolysis.
