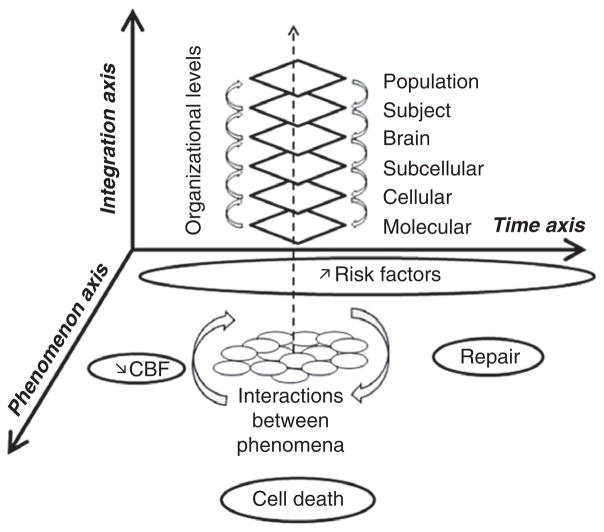
Fig. 1.
Schematic showing the nonlinear and highly integrative aspects of stroke pathophysiology. Mechanisms can be manifested at multiple levels of phenomenology, ranging from molecular and cellular biology to whole animal physiology and pharmacology to individual human subjects and population responses. The influence of genetics and risk factors adds to this complexity. And ultimately, these multifactorial processes connect into spatial and temporal gradients of tissue injury and repair. Altogether, this matrix represents a series of hurdles that must be considered before translation can take place. Finding clinically effective therapeutics for stroke prevention, treatment, and recovery is challenging. Multitarget integrative solutions may be required.