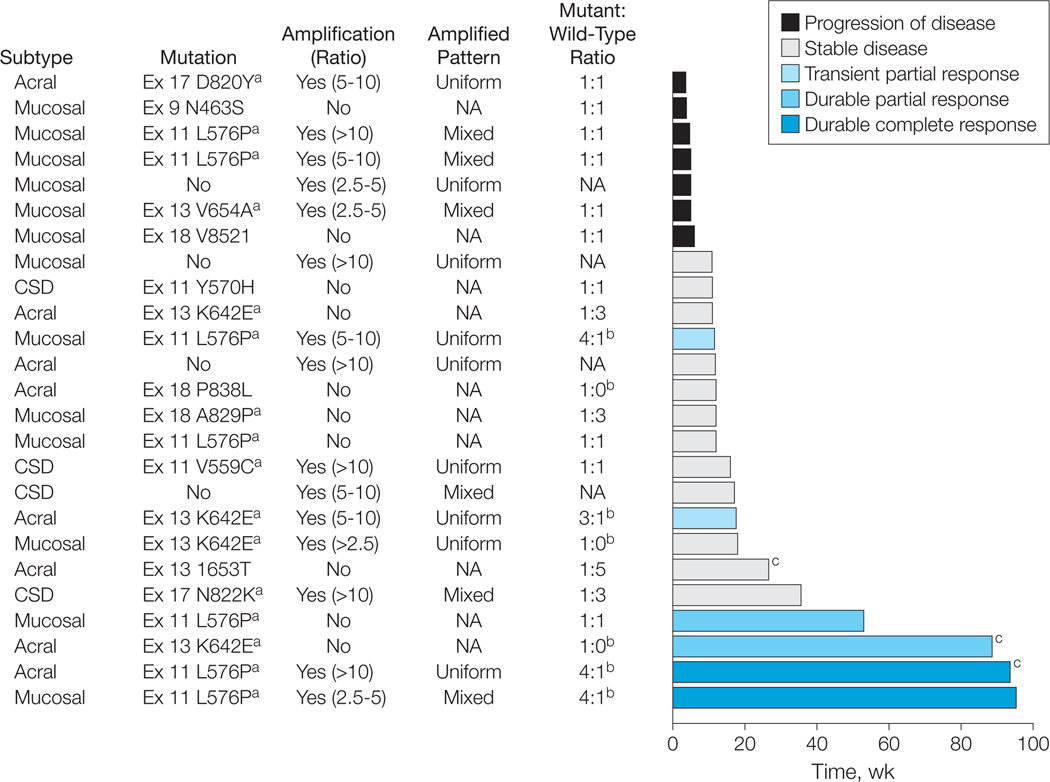
Figure 1. Treatment Response Over Time by Melanoma Subtype and Genetic Alteration of KIT.
CSD indicates melanoma arising from chronically sun-damaged skin; NA, not applicable. The melanoma subtype, KIT mutational and amplification status, the ratio of mutant to wild-type alleles as determined by their respective electropherogram peak heights, and the RECIST (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors) response achieved for each patient treated with imatinib mesylate is shown. Amplification was defined as a KIT-to-centromere ratio of 2.5 or more, with the pattern of amplification described as uniform (homogeneous) or mixed (heterogeneous) across the tumor specimen. The best response as determined by RECIST is identified by the color of the bar. The length of the bar represents the duration of time in weeks that each patient remained receiving therapy.
a Mutations previously identified in melanoma8,9 and gastrointestinal stroma tumors.35,36
b Tumors with mutant to wild-type allelic ratios of more than 1:1, which are those hypothesized most likely to respond to therapy with KIT inhibition.
c Patients receiving treatment at the time of this report.