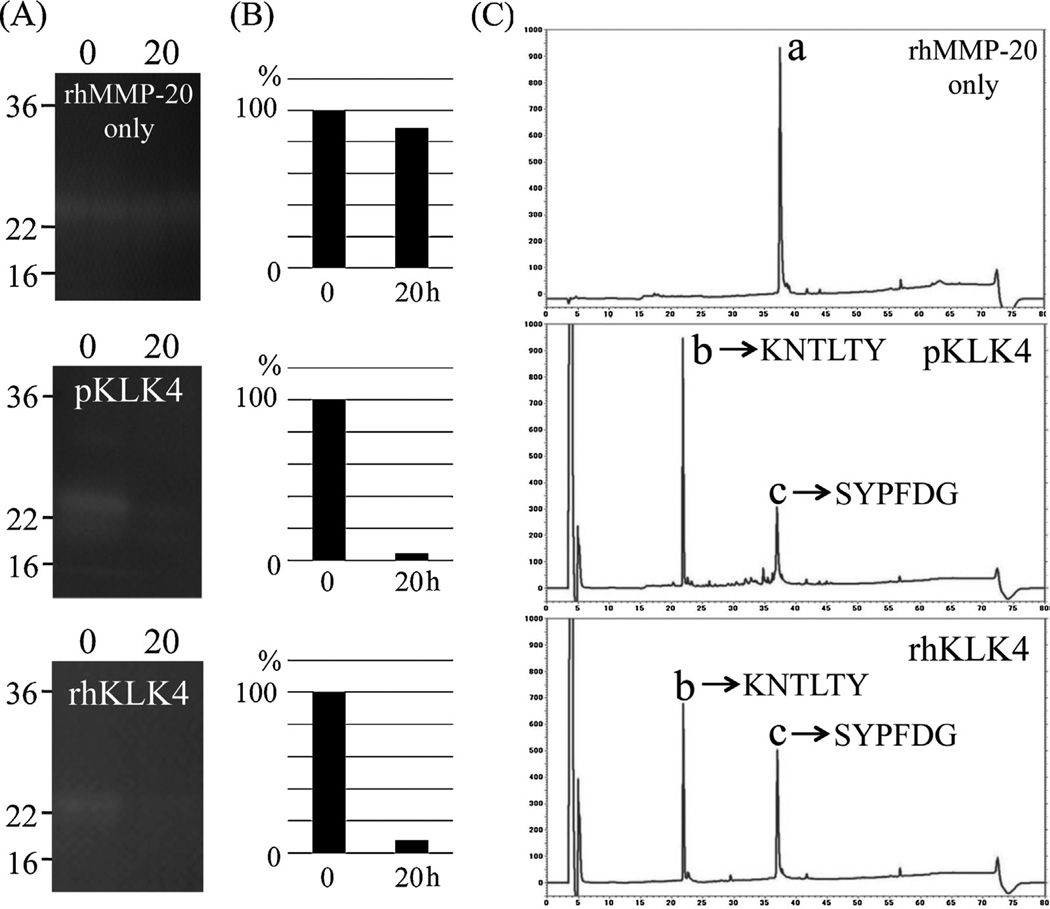
Fig. 6.
Inactivation of recombinant human MMP20 (rhMMP20) (substrate) by KLK4. (A) Both native porcine KLK4 (pKLK4) and recombinant human KLK4 (rhKLK4) activated by rhMMP20 were used to digest rhMMP20 for 0 or 20 h. The rhMMP20 alone was incubated for 20 h as a control and no degradation occurred before and after the incubation (top). Both pKLK4 (centre) and rhKLK4 (bottom) cleaved rhMMP20 and exhibited almost no activity on a casein zymogram after 20 h. (B) Quantification analysis of active bands before and after incubation. The active bands were normalized to the density of the 0 h band. (C) The digestion of (rhMMP20) was clearer on the chromatographic peaks of intact MMP20 and its digestion products after incubation with KLK4. C-18 RP-HPLC chromatograms after the digestion for 20 h showing rhMMP20 original material (a) with a retention time of 37.5 min; the generation of peaks (b) and (c) with retention times of 22 and 37 min after digestion with pKLK4 and rhKLK4. The protein sequences for the generated MMP20 peaks (b) and (c) are provided on the chromatograms.