Fig. 1.
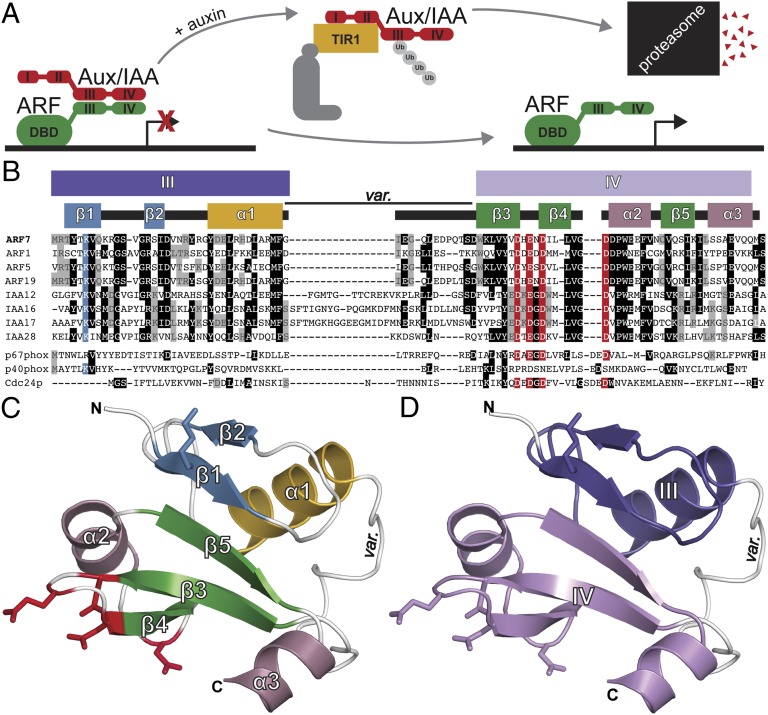
ARF7 contains a C-terminal type I/II PB1 domain. (A) In the current auxin-signaling model, Aux/IAAs dimerize with and repress ARF transcription factors in the absence of auxin. In the presence of auxin, Aux/IAAs interact with SCFTIR1 resulting in repressor degradation, freeing ARFs for auxin-responsive gene transcription. (B) Sequence alignment of ARF and Aux/IAA proteins identify canonical PB1 domain features, including a conserved lysine (blue) and the OPCA-like motif (red) that align with type I (p67phox and Cdc24p) and type II (p40phox) PB1 domains. The ARF and Aux/IAA PB1 domain variable region (var.) is also indicated. (C) The ARF7PB1 crystal structure reveals that the ARF7 C terminus is a PB1 domain. Secondary structure features are labeled and colored as in B with modeled lysine (blue) and OPCA (red) residues shown as stick representations. (D) ARF7PB1 structural features define ARF and Aux/IAA sequence motifs III and IV, which are colored as in B.