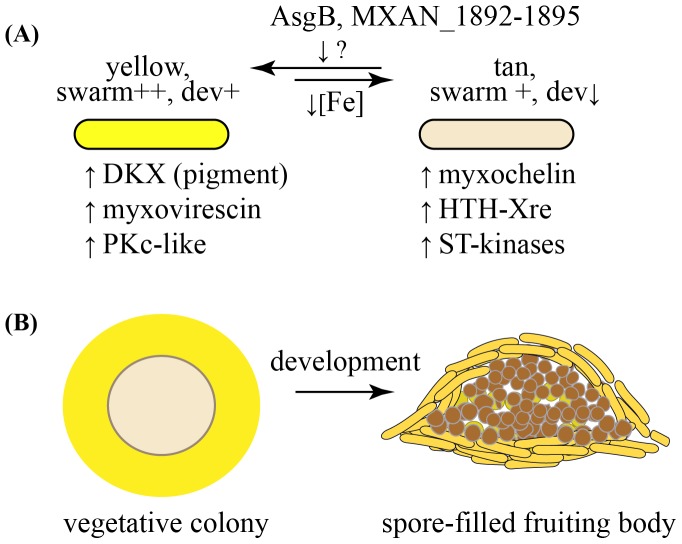
Figure 8. Phase variation yields two cell types.
(A) The data show that the concentration of iron influences the yellow to tan phase switch; in this model, we propose that AsgB or AsgB-dependent products play a key role in the reverse direction switch. The yellow variants produce myxovirescin, the antibiotic needed for predation [23]. Tan variants are mediocre swarmers but are more adept at sequestering iron. (B) The division of labor between yellow and tan variants may be critical for survival of M xanthus in nature. The robust yellow swarmers are enriched at the periphery of a WT colony whereas slow swarming tan variants would be more enriched at the colony center. The ramifications for development are clear: tan cells, which are predisposed to become spores are well positioned to end up in the interior of the fruiting body and are surrounded by cells that produce DKX, the pigment needed to for production of viable spores [13].