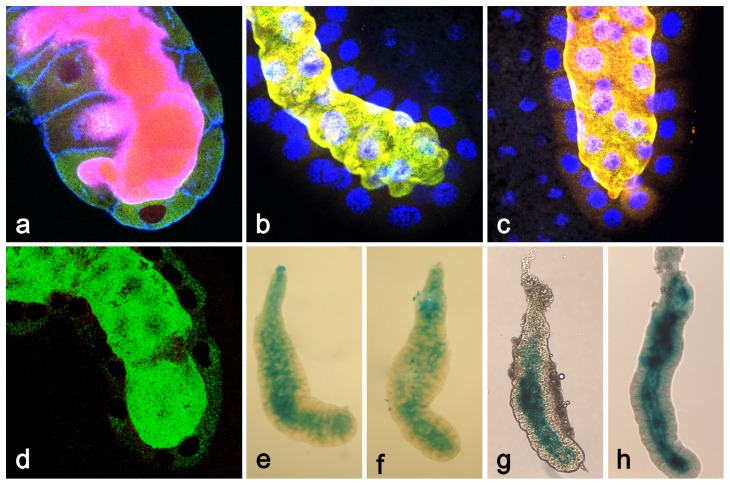
Figure 5. A great variety of proteins are detected by antibody, GFP-/EYFP-/RFP-fusion constructs, or X-Gal staining for active β-galactosidase produced by lacZ-containing P-element insertion stocks.
We consistently used 9–10 hr old prepupal salivary glands for these types of detection. (a) Salivary gland showing the presence of nuclear receptor E75 (red) and a portion of the cytoplasmic signaling protein Ras2 (green) in the lumen. The cortical membrane is stained with AF488-phalloidin for F-actin. (b) Similarly to (a), two cytoplasmic proteins, Oho-31 (green) and tight junction membrane protein Arm (red) were found secreted into the lumen; nuclei are stained for DNA with Hoechst 33258 (blue). (c) Tumor suppressor protein p127, the product of l(2)gl gene (green), and the nucleolar component fibrillarin (red) are found secreted in the lumen; nuclei are stained for DNA with Hoechst 33258 (blue). Fluorescently-tagged constructs (most using GFP-), showed that many fusion proteins were secreted into the lumen. These are exemplified by GFP-Rbp1 (d). Examples of proteins monitored via lacZ-fusion include the transcription factor Ttk (e), the dual-specific LAMMER kinase Doa (f), the D subunit of the vacuolar H+ vATPase Vha36-1 (g) and the transcription factor Fkh (h).