Figure 1.
Development of an In Vitro Clonal Multipotency Assay
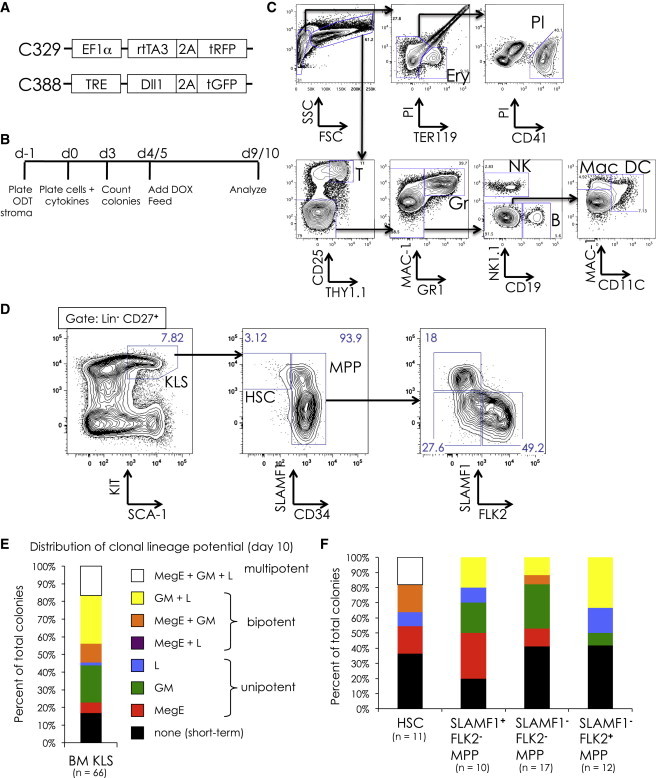
(A) Lentiviral constructs used to generate a tetracycline-inducible Dll1 OP9 stromal line (ODT). Construct C329 (top) drives constitutive expression of the tetracycline-inducible transactivator rtTA3. Construct C388 allows induction of Dll1 expression when the transactivator is activated in the presence of doxycycline (DOX).
(B) Strategy for clonal assay. ODT stroma is plated the day prior to cell sorting (day −1). At day 0, cells are clone sorted directly onto ODT stroma and cytokines are added (SCF, TPO, EPO, Flt3L, IL-7, and IL-15). At day 3, hematopoietic colonies are counted. At day 5, cells are fed and Flt3L, IL-7, IL-15, and DOX (1 μg/ml) are added. At day 9 or 10, colonies are harvested and analyzed by FACS.
(C) Representative hematopoietic output at day 10 of culture of unsorted e12.5 FL. Representative examples of multipotent output from single-cell cultures can be found in Figure S1.
(D–F) Testing multipotency assay on adult bone marrow (BM) stem/progenitor cells. (D) Sort gates for KIT+ Lin− SCA-1+ (KLS) cells and subpopulations of KLS, including HSCs (CD34−, SLAMF1+) and three fractions of multipotent progenitors (MPP) are shown. (E) The distribution of lineage potential of colonies from adult BM KLS cells, showing cells that produced a single branch (MegE in red, GM in green, and L in blue), two branches (MegE + GM in orange, GM + L in yellow, and MegE + L in purple), and all three branches (MegE + GM + L in white). Cells that produced lineages from all three branches (white) were scored as multipotent. Cells that gave rise to colonies that did not survive to day 10 are shown in black. The number of hematopoietic colonies scored (n) is indicated. (F) Distribution of lineage potential in colonies derived from sorted KLS subpopulations. Note that only HSCs gave multipotent (white) readout.
