Figure 1.
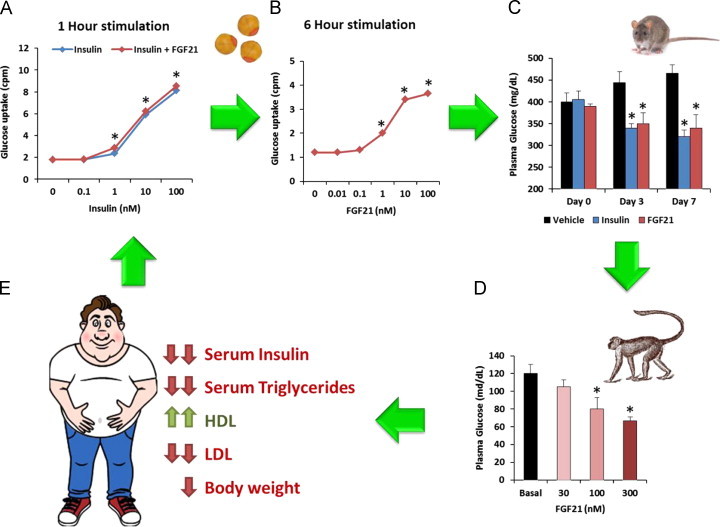
Schematic representation of the identification and evaluation of FGF21 therapeutic utility through the drug discovery process. (A) The functional screening assay involved the assessment of FGF21's effects on glucose uptake in combination with insulin utilizing in an adipocyte model. (B) Following the initial activity hit the glucose uptake screening system was refined to more accurately capture the magnitude of FGF21 action in a longer term treatment paradigm. (C) Subsequent work focused on demonstrating translatability of this in vitro effect into metabolic efficacy in rodent models of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia such as ob/ob mice, where FGF21 demonstrated glucose lowering comparable to that observed with insulin (A, B and C are adapted from [8]). (D) The next study confirmed that FGF21 is bioactive in diabetic non-human primates, a model of metabolic disease which closely resembles the human condition (adapted from [40]). (E) Finally, LY2405319, an FGF21 analog, was shown to be efficacious in humans, suggesting that FGF21-based therapies may indeed represent a novel therapeutic option [49].
