Fig. 3.
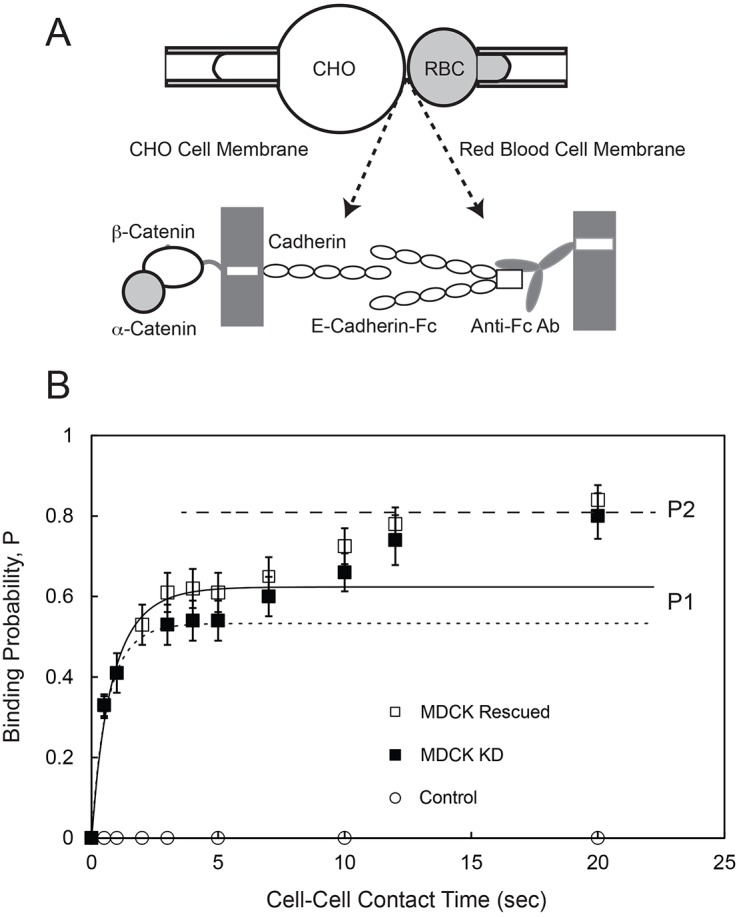
Kinetics of E-cadherin-mediated binding between an MDCK cell and an RBC modified with E-cad-Fc. (A) Schematic of the micropipette aspiration experiment. A cell expressing full-length cadherin is aspirated into a pipette (left) and repetitively brought into contact with an RBC modified with Fc-tagged canine E-cadherin extracellular domains (E-cad-Fc), which are captured and oriented by anti-Fc antibody covalently bound to the RBC (right). (B) The time-dependent binding probability (P) versus cell–cell contact time measured between RBCs modified with E-cad-Fc and MDCK KD cells (black squares) or MDCK Rescued cells (white squares). The solid line is the nonlinear least squares fit of Eqn 1 to data for the first binding step obtained with MDCK Rescued cells, with best-fit parameters given in the text. The dotted line is the fit to data obtained with MDCK KD cells, with best-fit parameters given in the text. The dashed line indicates the limiting binding probability P2 determined with both MDCK Rescued and MDCK KD cells. Control data (white circles) were measured between MDCK Rescued cells and RBCs modified with anti-human IgG (Fc) antibody without bound E-cad-Fc.
