Figure 6.
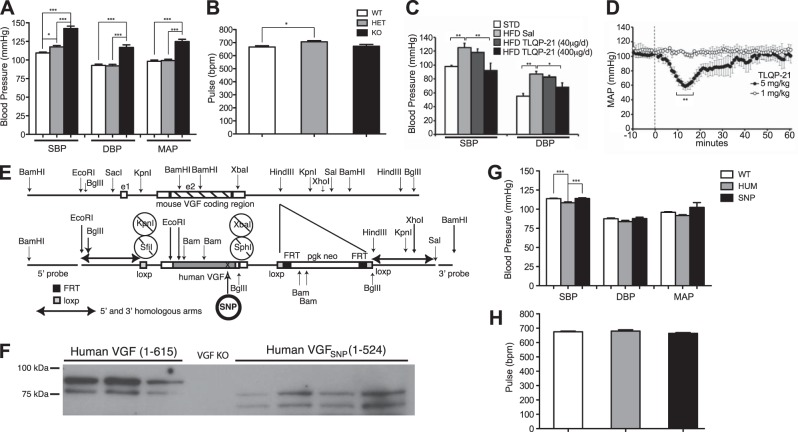
Germline VGF ablation increases BP that is rescued by germline knock-in of human VGF1–615 into the mouse Vgf locus, consistent with reduced BP in VGF peptide TLQP-21-treated mice and rats. A, B) BP (A) and pulse (B) were recorded utilizing tail plethysmography in awake wild-type Vgf+/+, heterozygous-knockout Vgf+/−, and homozygous-knockout Vgf−/− mice, as described in Materials and Methods. SBP, DBP, MAP, and pulse (bpm) are shown, and SBP, DBP, and MAP were significantly increased in Vgf−/− (KO) compared to Vgf+/+ (WT) and Vgf+/− (HET) mice (means±sem; n=9–12 mice/group). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0001; 1-way ANOVA. C) Chronic 14-d treatment of obese, hypertensive mice with TLQP-21 (400 μg/d) decreased SBP and DBP, recorded by intracarotid catheterization under anesthesia, while a lower dose of TLQP-21 (40 μg/d) was ineffective. STD, standard diet; sal, saline. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. HFD-sal group. D) Acute intravenous infusion of TLQP-21 (5 mg/kg) rapidly and transiently decreased MAP in freely moving Sprague-Dawley rats (F(61,122)=4.8, P<0.0001; n=4) measured by telemetry, while infusion of a lower dose of TLQP-21 (1 mg/kg) was ineffective (n=2). Dashed line marks peptide infusion. **P < 0.01 vs. baseline; ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc comparison. E–H) Germline knock-in of human VGF1–615 or an SNP-encoded, truncated human VGF1–524 into the mouse Vgf locus rescued the hypertensive phenotype resulting from germline VGF ablation. E) Gene-targeting strategy used to generate hVGF and SNP lines. F) Western blotting with anti-VGF antisera was used to identify full-length human VGF1–615 and truncated human VGF1–524 in total brain lysates from homozygous hVGF and SNP mice, respectively. G, H) SBP, DBP, and MAP (G) and pulse (bpm; H) were measured by tail plethysmography in awake wild-type (WT), and homozygous hVGF1–615 (HUM) and hVGF1–524 (SNP) mice (means±sem; n=9–12 mice/group). Note that SBP in homozygous hVGF1–615 is slightly but significantly lower than homozygous hVGF1–524 mice that lack TLQP-21 (G). ***P < 0.0001; 1-way ANOVA.