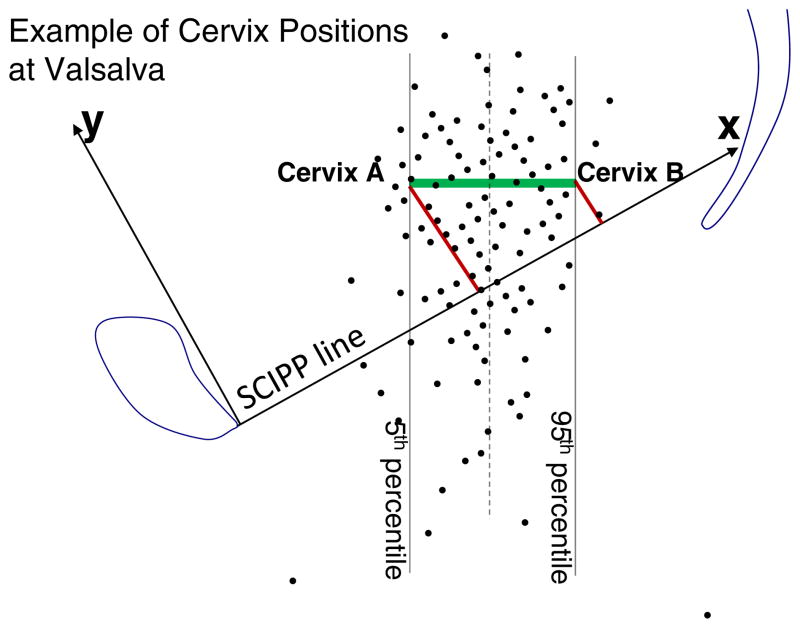
Fig 3.
The points represent the distribution of 149 cervix locations at maximum strain for an average θ-SCIPP line strain angle of 29°. Note that two cervices from this sample have the same cranio-caudal location, but different antero-posterior locations, so in the oblique reference system (SCIPP) the y coordinates will vary. The difference (Δ) in the “vertical” distance, v, is given by Δ v=Δ x * sin (θ). In this data set, Δx between the 5th and 95th percentiles of the horizontal cervix distribution was 3.3 cm, which resulted from a 1.6-cm difference in the y coordinate