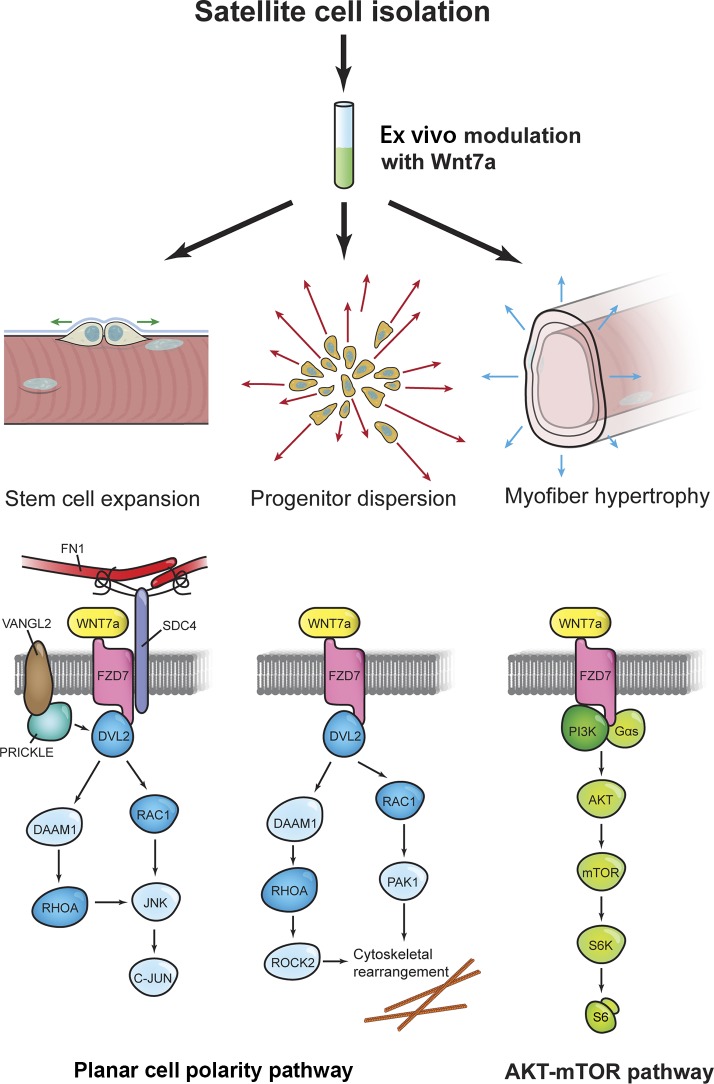
Figure 8.
Molecular mechanisms of ex vivo Wnt7a modulation. Upon stimulation, Wnt7a induces the symmetric proliferation of Myf5-independent satellite cells in conjunction with fibronectin (FN1), syndecan-4 (SDC4) and Vangl2 through the planar cell polarity pathway. In myogenic progenitors, Wnt7a also facilitates Rac1-mediated cell polarization and migration. Fusion of Wnt7a-treated cells activates the AKT–mTOR pathway, leading to myofiber hypertrophy. Therefore, Wnt7a acts on three levels to facilitate the outcomes of cell therapy: (1) it boosts stem cell number, (2) facilitates their dispersion in the host tissue, and (3) leads to muscle growth.