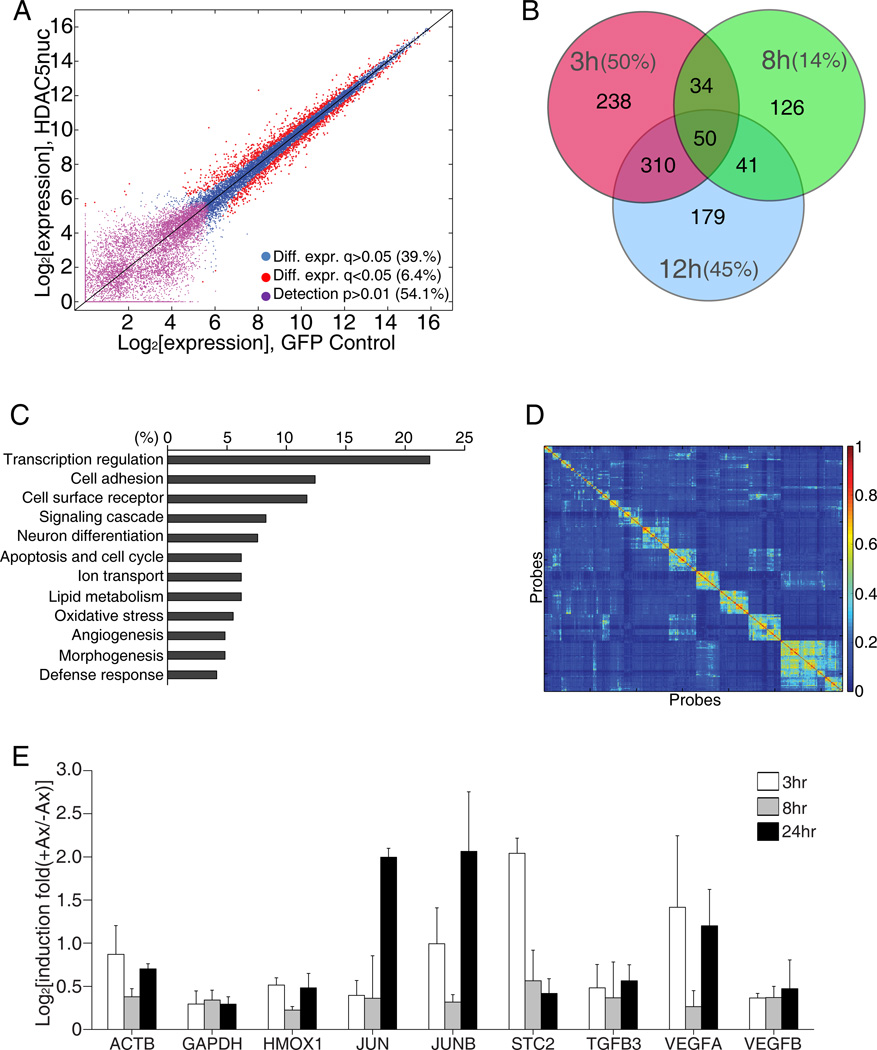
Figure 6. HDAC5 regulates transcriptional activation after injury.
(A) Dependence of basal gene expression on GFP-HDAC5nuc expression. Red dots: differentially expressed probes with FDR-corrected q-value<0.05 (1,637 probes, 6.4%), violet dots: probes below level of detection in both conditions (13,902, 54.1%), blue dots: remaining probes (10,158, 39.5%). (B) Venn diagram of HDAC5-dependent genes at the indicate time points after axotomy. The percentage of all genes at each time point that are HDAC5-dependent is indicated. (C) GeneOntology analysis of the HDAC5-depdendent genes shown in (B) at the 3 hours time point. (D) Heat map representation of the pairwise co-clustering frequency matrix of 646 expression vectors corresponding to 323 probes in GFP and GFP-HDAC5nuc expressing DRG neurons. Ordering of probes along horizontal and vertical axis based on hierarchical clustering. (E) Quantitative PCR analysis of mRNA samples extracted from mouse DRG that received a sciatic nerve axotomy 3, 8 or 24 hours prior to DRG dissection (n=3). See also Figure S3 and Table S1, S2 and S3.