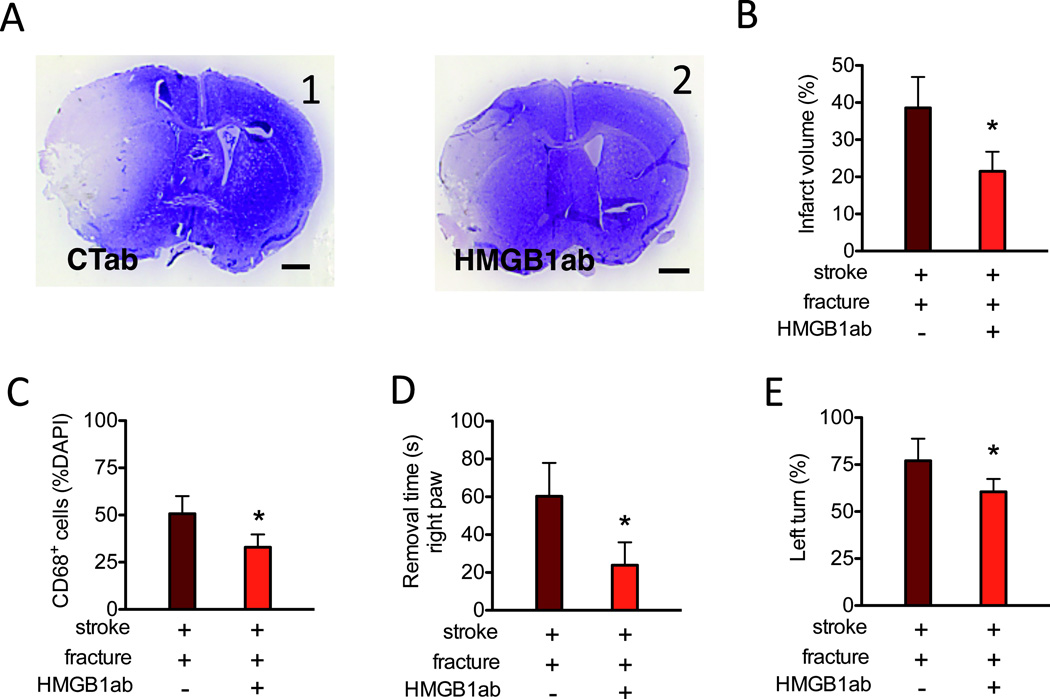
Figure 5. Neutralized HMGB1 antibodies attenuate the negative impact of bone fracture on stroke injury.
A. Representative images of cresyl violet stained brain sections (bregma 1.3 mm, scale bar: 1 mm) of stroke mice with bone fracture procedure receiving control antibodies (A1, CTab) or anti-HMGB1 antibodies (A2, HMGB1ab). B. The bar graph shows quantification of the infarct volumes (n=7, *: P<0.001). C. Quantification of CD68+ cells in the peri-infarct region (n=6, *: P<0.001). D. Adhesive removal time of the right paw of mice treated with CTab or HMGB1ab (n=10, *: P<0.001). E. Percentage of left turn in the corner test of mice treated with CTab or HMGB1ab (n=10, *: P<0.001). CTab: Control antibody; DAPI: 4',6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole; HMGB1ab:High-mobility-group box chromosomal protein-1 neutralized antibody.