Fig. 5.
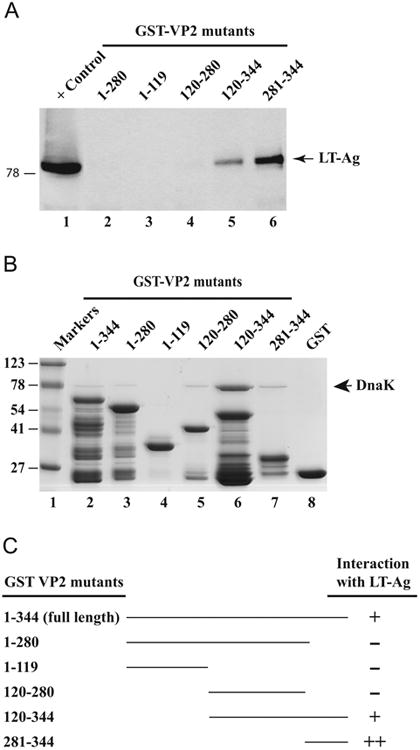
Localization of the domain(s) of VP2 that interacts with LT-Ag. (A) GST-VP2, and N-terminal and C-terminal VP2 deletion mutants immobilized on GSHSepharose 4B beads were incubated with whole-cell extract prepared from HJC-15b cells (Raj et al., 1995) for 2 h at 4 °C as described in Material and methods. The Sepharose beads were washed extensively and proteins interacting with GST or GST-VP2 or GST-VP2 mutants were separated on a SDS-10% PAGE and analyzed by western blotting with an anti-LT-Ag antibody (Ab-2, monoclonal). (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of GST, GST-VP2 and, GST-VP2 N-terminal and C-terminal deletion mutants. (C) Summary of the results obtained from in vitro mapping assays (from Fig. 3C and Fig. 5A). The abilities of VP2 and its deletion mutants to interact with LTAg are shown on the right (+, specific interaction; -, no interaction, ++, enhanced interaction). The positions of molecular weight markers (in kilodaltons, kD) are shown to the left of panel B.
