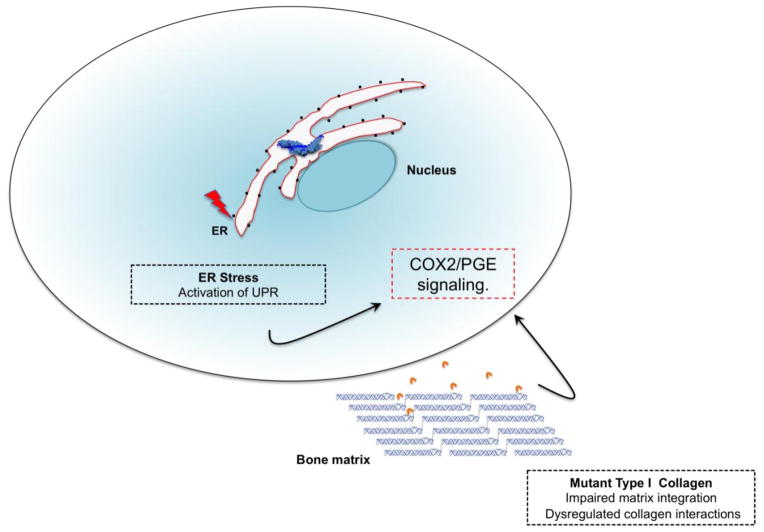
Figure 3. Hypothetical model representing pathogenetic mechanisms underlying Caffey Disease.
The R836C mutant proα1(I) chains may induce ER stress triggering an unfolded protein response leading to an upregulation of the COX2/PGE axis. Alternatively, the R836C mutant type I collagen fibrils may disrupt ligand interactions within the ECM resulting in signaling events that either directly or indirectly lead to elevated COX2/PGE signaling and altered resident cell function.