Fig. 1. Immunoglobulins selectively bind to proteins in human mycoplasma.
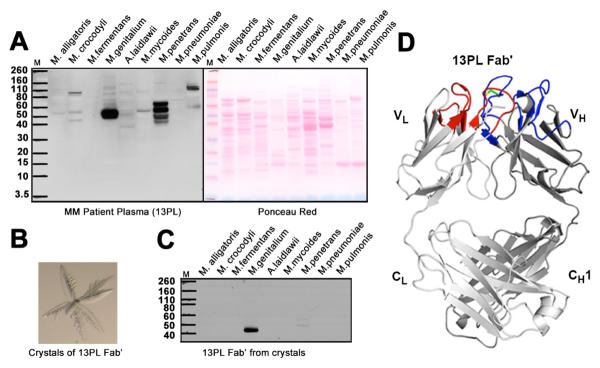
(A) (Left panel) Western blot analysis of the reactivity of plasma from multiple myeloma patient 13PL with cell extracts from Mycoplasma alligatoris, Mycoplasma crocodyli, Mycoplasma fermentans, M. genitalium, Acholeplasma Mycoplasma laidlawii, Mycoplasma mycoides, Mycoplasma penetrans, Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pulmonis. All mycoplasma cells were grown in appropriate media. Cells were lysed according to manufacturer's protocol using lysis buffer from Sigma Aldrich. Nucleic acids were degraded by treatment with DNAase and RNAase. A protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche) was added to prevent proteolytic degradation. The extracts from the same number of cells were separated on SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes for Western blot analysis. (Right panel) Ponceau red-stained protein bands of the cell extracts. (B) Crystals of 13PL Fab' from a multiple myeloma patient's monoclonal immunoglobulin. (C) Western blot analysis of the reactivity of 13PL Fab' from the plasma of a multiple myeloma patient with the same cell extracts in A. The 13PL Fab' was purified by crystallization. The extracts were separated on SDS-PAGE gels as described in (A). (D) Crystal structure of 13PL Fab' shown in ribbon diagram with the light and heavy chains colored in light and dark gray, respectively. The loops corresponding to CDRs L1, L2, and L3 are colored blue, whereas CDRs H1, H2, and H3 are colored red. The relatively rare disulfide in human CDR3's is colored green.
