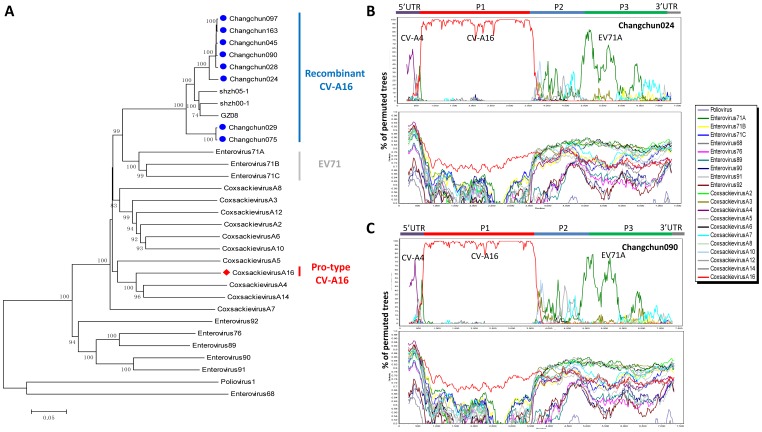
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of eight CV-A16 full-length genomic sequences isolated from HFMD patients in Changchun, China.
(A)The complete genomic sequences of 3 other CV-A16 strains from China and all of the 21 HEV reference sequences were retrieved from Genbank. Phylogenetic analysis was conducted using MEGA4 software employing the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 replications and the Kimura 2-parameter model. Bootstrap values greater than 70% are shown. The ▪icon indicates CV-A16 strains isolated from Changchun; the ♦icon indicates the prototype CV-A16-G10. (B) and (C) Identification of recombinant circulating CV-A16 strains of Changchun024 and Changchun029 by bootscanning. (B) Bootscanning analysis of Changchun024 as the query sequence. (C) Bootscanning analysis of Changchun029 as the query sequence. For all HEV-A sequences together with other two outgroups EV68 and poliovirus 1, Changchun024 and Changchun029 showed possible recombination with CA4, CV-A16-G10, and EV71A. Bootscanning was generated with Simplot 3.5.1 software using a sliding window size of 500 bases and step size of 20 bases at a time. The y axis shows the percentage of the permuted tree in which the selected HEV virus sequences cluster with the query sequence.