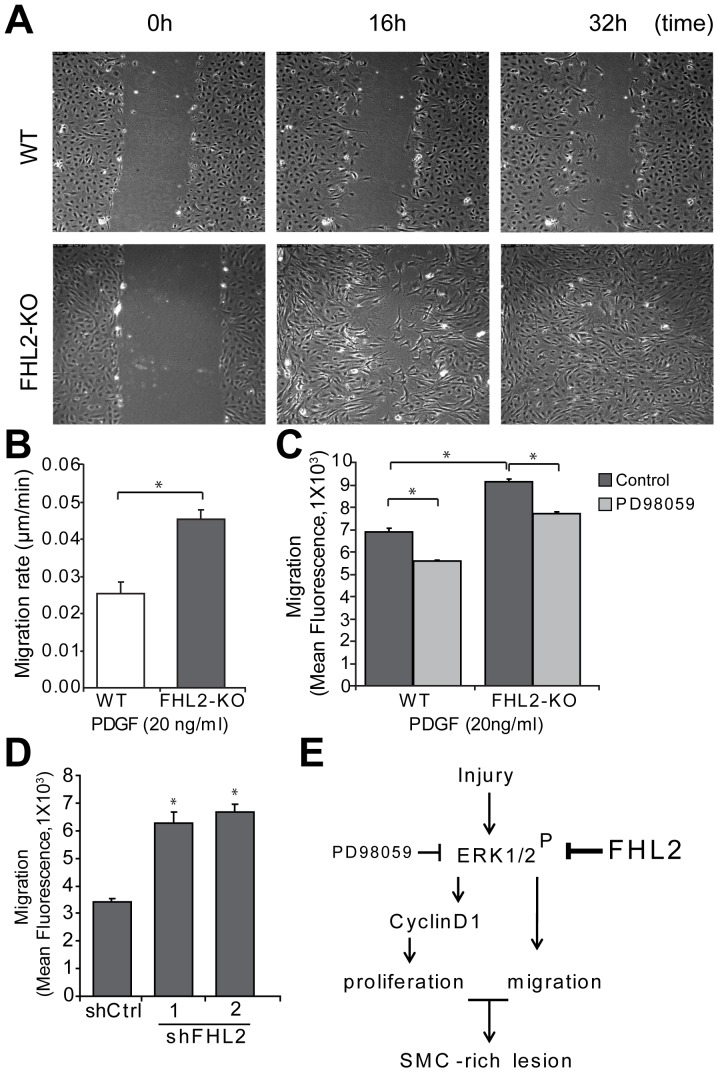
Figure 5. FHL2-KO SMCs migrate faster.
A, A scratch was made in a confluent layer of serum-starved SMCs that were stimulated with PDGF (20 ng/ml). Images were captured every 10 min using a live cell microscope and representative images at 0, 16 and 32 h are shown. Movies of the movement are in the online supplement. B, Quantitative analysis of SMC migration in the scratch wound assay showing that FHL2-KO SMCs migrated 1.8 fold faster than WT SMCs. C, SMCs were treated with or without PD98059 and cell migration was evaluated using a trans-well assay. Cells were labeled with a fluorescent dye and seeded in the upper chamber. Cell migration was measured as fluorescence after 3 h. D, SMC migration was evaluated using a trans-well assay after knock-down of FHL2 using lentiviral particles encoding shCtrl, shFHL2#1 and shFHL2#2 in WT SMCs. Cell migration was measured as fluorescence after 3 h. Data represent means±SD. *P<0.05 for shCtrl versus shFHL2. E, Schematic representation of FHL2 function in the modulation of SMC-rich lesion formation. FHL2 modulates SMC-rich lesion formation by inhibiting proliferation and migration of SMCs via the ERK1/2-CyclinD1signaling pathway.