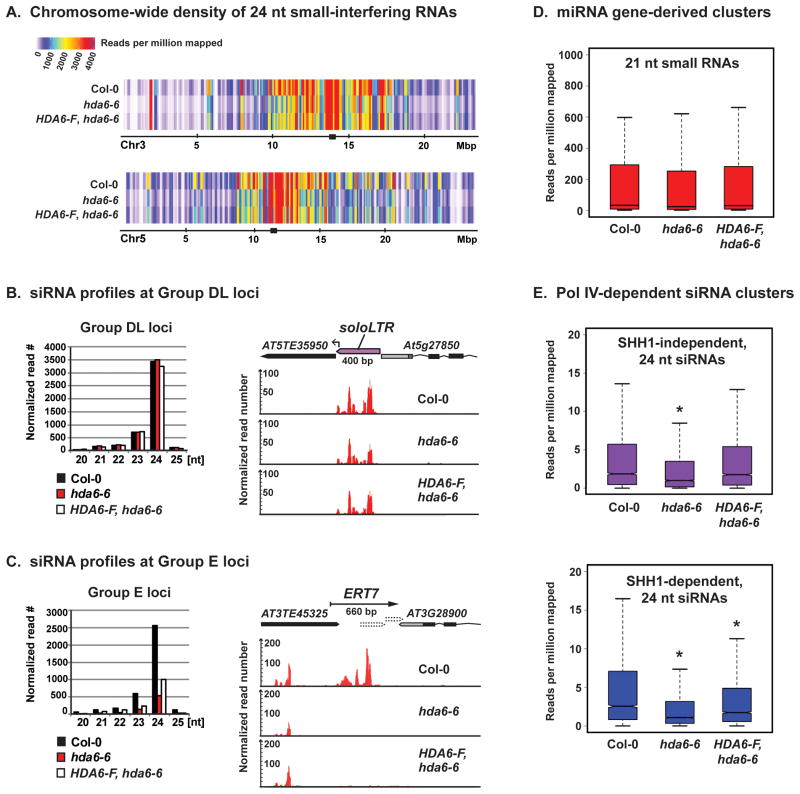
Figure 6. Epigenetic memory loss results in failure to produce Pol IV-dependent siRNAs.
(A) Abundance of 24 nt siRNAs mapping to chromosomes 3 and 5 in wild-type (Col-0), hda6-6 and HDA6-FLAG rescued hda6-6 plants. Small RNA clusters are plotted using a 200-kb sliding window stepped in 100-kb increments. Black squares mark the estimated positions of centromeres.
(B) Relative abundance of siRNAs of different size classes mapping to Group DL loci (left panel) and a browser view of siRNA abundance and distribution at the soloLTR locus (right panel).
(C) Relative abundance of siRNAs of different size classes mapping to Group E loci (left panel) and a browser view of siRNA profiles at ERT7 (right panel). Supporting polyA+ RNA-seq data and gene annotations are in Figures 4A and S4.
(D) Boxplot analysis of 21 nt miRNAs, revealing no significant overall change in miRNA abundance in hda6 or hda6 HDA6-F rescue lines relative to wild-type Col-0.
(E) Boxplot analysis of the effects of HDA6 mutation, and HDA6 rescue, on 24 nt siRNAs that are either SHH1-independent or SHH1-dependent (as defined in Law et. al. 2013). All read counts are normalized to total mapped read numbers. Asterisks above boxplots in panel E indicate significant reduction relative to Col-0 (p < 0.002, Wilcoxon rank-sum test). See also Figure S7.