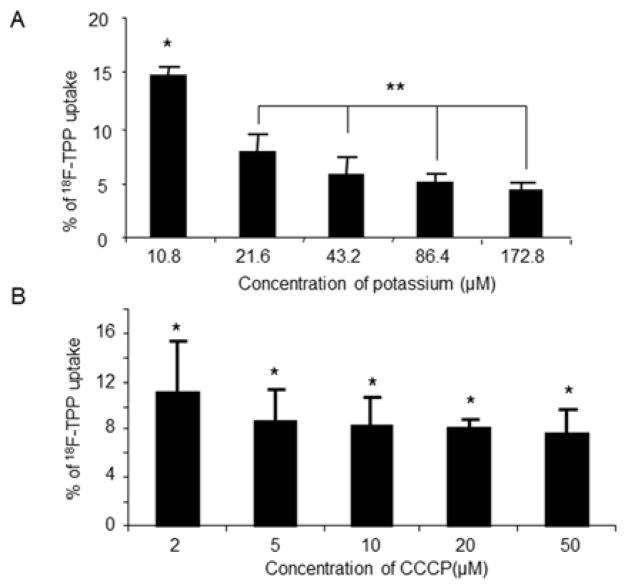
Fig. 2. Effects of potassium and CCCP concentrations on 18F-TPP uptake by PC-3 cells.
The uptake of 18F-TPP was decreased as the extracellular potassium concentration increased. At the highest potassium concentration of 172.8 μM, the uptake was the lowest, while at the lowest potassium concentration of 10.8 μM, the uptake was at the highest. An inverse linear correlation between the uptake and extracellular potassium concentration (slope: 0.62+/− 0.78; correlation coefficient: r=0.936+/− 0.11) was found (Fig. 2 A: ANOVA, * vs. **: P<0.05; ** P>0.05). Gradually increased concentrations of CCCP lead to decreased uptakes of 18F-TPP, which quickly reached a trough at CCCP concentration of 5μm (Fig. 2 B: ANOVA, * P>0.05).