Figure 3.
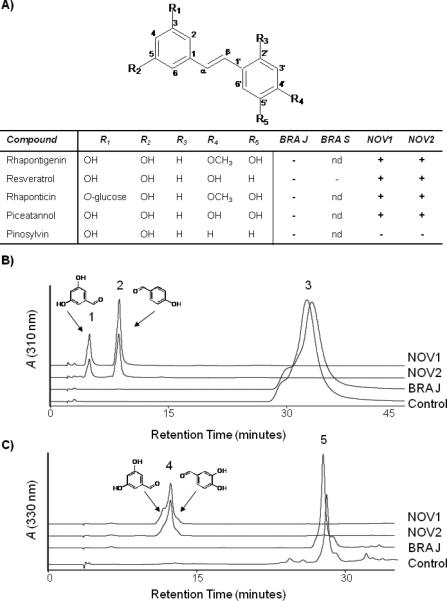
In vitro cleavage of stilbene compounds. A) Stilbene compounds with different functional groups were chosen as substrates for in vitro assays with NOV1, NOV2, BRA-J, and BRA-S protein lysates. Cleavage of the substrates is indicated by a + in the table based on product identification by HPLC and LC-MS. None of the enzymes cleaved pinosylvin. B) HPLC analysis of in vitro assays with resveratrol as a substrate. Synthesis of 3,5-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (1) and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde cleavage products (2) from 1 mM resveratrol (3) with NOV1 and NOV2 protein extracts. No residual resveratrol was detected by HPLC or LCMS. C) HPLC trace of in vitro assay with piceatannol as a substrate. Synthesis of 3,5-dihydroxybenzaldehyde and 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde cleavage products (4) from 1 mM piceatannol (5) with NOV1 and NOV2 enzymes protein extracts. Small amounts of residual piceatannol could be detected for NOV2. BRA-J protein extracts did not produce cleavage products with either resveratrol or piceatannol. Protein extracts from E. coli served as a control.
