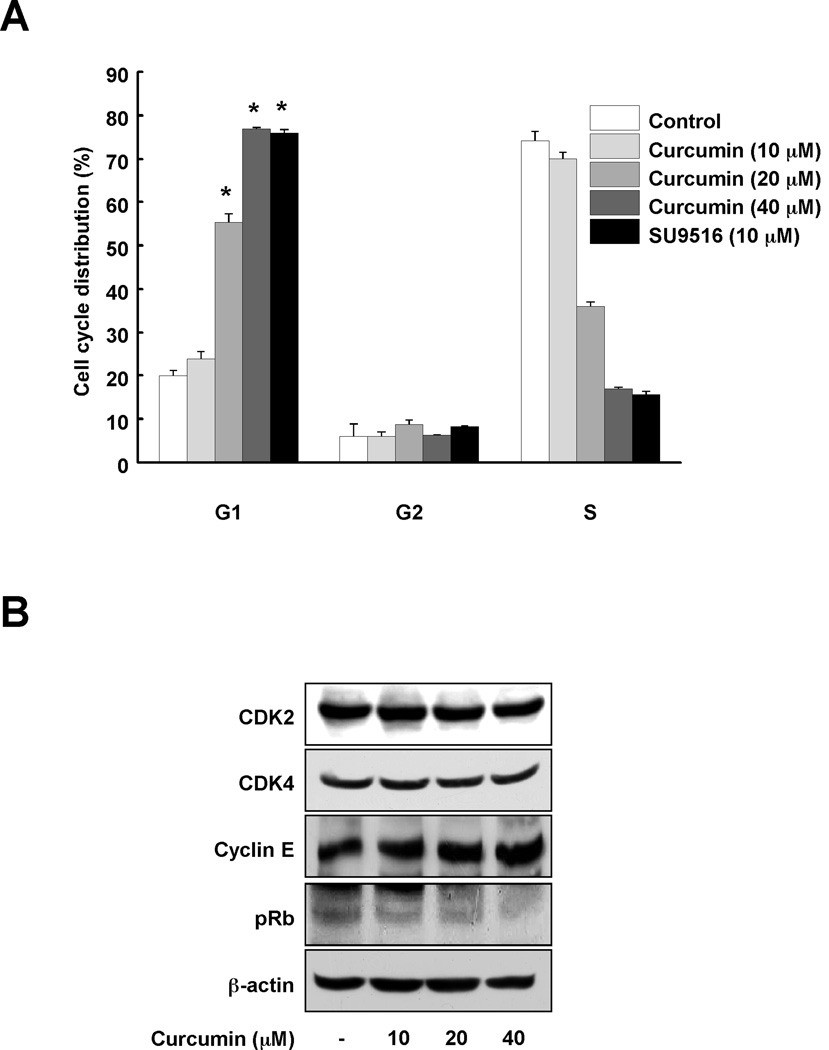
Fig. 4.
Curcumin induces G1 arrest in HCT116 colon cancer cells. (A) The effect of curcumin on cell cycle was investigated using flow cytometry. HCT116 colon cancer cells were cultured until they reached confluence in 96-well plates and then synchronized in G0 phase by serum deprivation. After 9 h of treatment with curcumin (0, 10, 20, or 40 µM) or SU9516 (10 µM), cell cycle phases were analyzed. Data are represented as means ± S.D. as determined from 3 independent experiments and the asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.001) compared to untreated group. (B) To determine the effect of curcumin on cell cycle proteins, Western blotting was performed using specific antibodies. After synchronizing the cells for 12 h, cells were treated with the indicated concentration of curcumin for 30 min. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments that gave similar results.