Fig. 4. Biochemical and immunohistochemical characterization of the B. terrestris male head glands and their comparison with head glands of females.
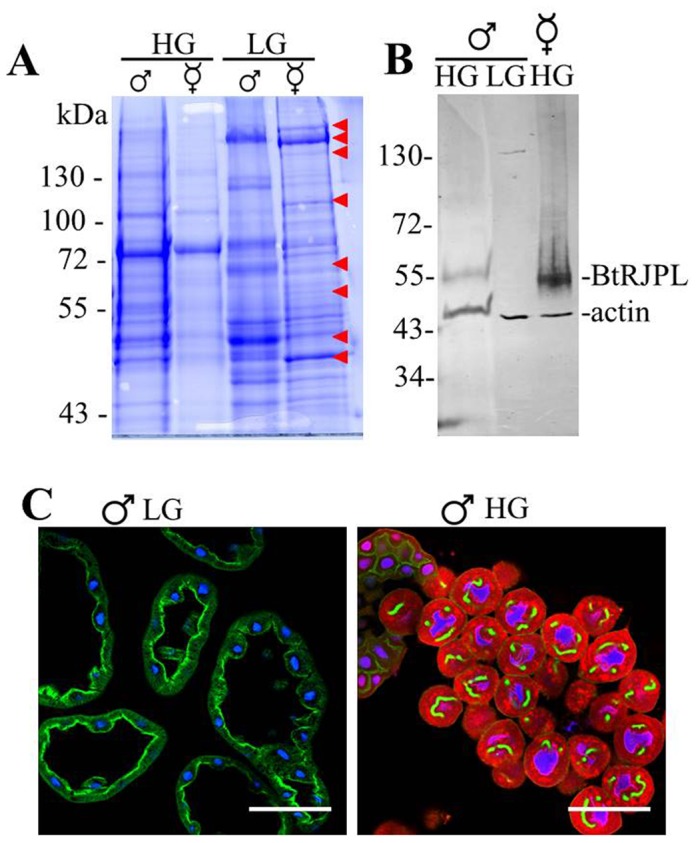
(A) Protein profiles. Proteins of hypopharyngeal and labial glands were size-separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. Protein profiles of male and female HGs are similar, those of LGs show sex-specific differences. Red arrowheads point to some of the protein bands differing between male and female LGs. Observed differences suggest different functions of male and female LGs. (B) BtRJPL is express in male HGs but absent in LGs. Actin (as a control protein) was detected by immunoblotting of size-separated protein extracts of both HGs and LGs. Male HGs extract is a pool of six HGs. Female HGs extract represents 20% of total HGs of a single worker. (C) Histology of male LG (left) and HG (right) secretory acini. LG acini are build-up of multiple cells forming an epithelial sac, the acini of HG are unicellular. Blue: nuclei (Hoechst), green: phalloidin-labeled F-actin, red: BtRJPL. Scale bars: 100 µm.
