Fig. 4. Reciprocal tests for interactions between mutant and wild-type receptors in the trypsin digestion assay.
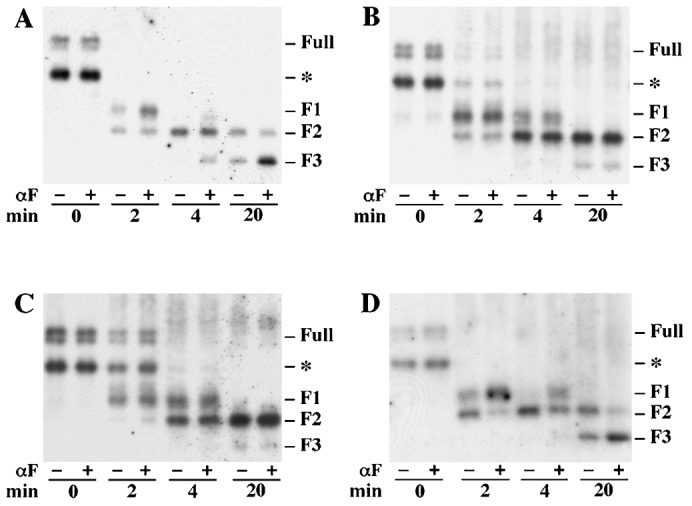
Membranes were incubated with trypsin in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 10−8 M α-factor (αF). Antiserum was against the T7 epitope-tag fused to the N-terminus of the receptors. Two major glycosylation sites (position 25 and 32) on T7-tagged Ste2 have been removed by genetic manipulation for experimental convenience. (A) Membranes were from cells expressing untagged wild-type Ste2 and T7-tagged Ste2-N25Q,N32Q (strain DJ213-7-3 containing plasmid pDJ656). (B) Membranes were from cells expressing untagged wild-type Ste2 and T7-tagged Ste2-F204S-N25Q,N32Q (strain DJ484-1containing plasmid pDJ657). (C) Membranes were from cells expressing T7-tagged Ste2-F204S-N25Q,N32Q (strain DJ213-7-3 containing plasmid pDJ657). (D) Membranes were from cells expressing untagged Ste2-F204S and T7-tagged Ste2-N25Q,N32Q (strain DJ482-1 containing plasmid pDJ656). The resulting cleavage products were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using anti-T7 antiserum. Three major cleavage products (F1, F2 and F3) are indicated at the right. Time points for treatment of trypsin are indicated on the bottom. All untagged receptors were synthesized under the direction of the GPD transcriptional promoter.
