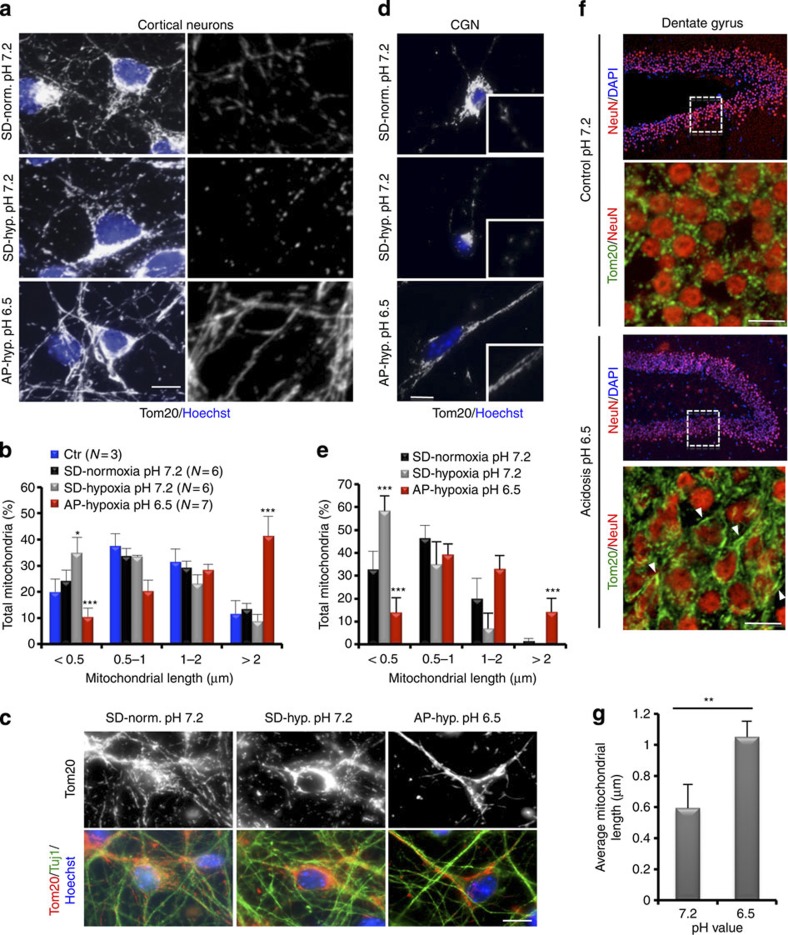
Figure 1. Extracellular acidification restructures mitochondria in post-mitotic cells.
(a) Representative confocal images of mitochondrial morphology in cultured cortical neurons following 18-h incubation at normoxic (Norm.) or hypoxic (Hyp.) conditions in SD or AP media. Mitochondria were visualized by Tom20 immunofluorescence. Panels on the right represent zoomed views of the mitochondria. (b) Mitochondrial length from (a) was quantified and binned into different length categories. Represented as mean and s.d. (n values indicated on graph). Ctr=control; represents neurons incubated in neurobasal media. (c) Representative images of mitochondrial morphology, revealed by Tom20 staining, in Tuj1+ cortical neurons at the indicated conditions. (d and e) Mitochondrial morphology in cultured CGN after 18-h incubation at the indicated conditions. Insets in (d) are zoomed views of mitochondria. (e) Mean and s.d. (n=3) of mitochondrial length data in (d). (f and g) Mitochondrial morphology in ex vivo hippocampal slice preparations incubated in normoxia for 4 h at the indicated conditions. Neurons were immunostained with NeuN (neuronal-specific nuclear protein) and Tom20 (mitochondria). Panels showing Tom20/NeuN staining are zoomed views of the boxed area within the hippocampus. Arrowheads indicate elongated mitochondria. (g) Average mitochondrial length and s.d. were plotted for the indicated conditions. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (Student’s t-test). For all images scale=10 μm.