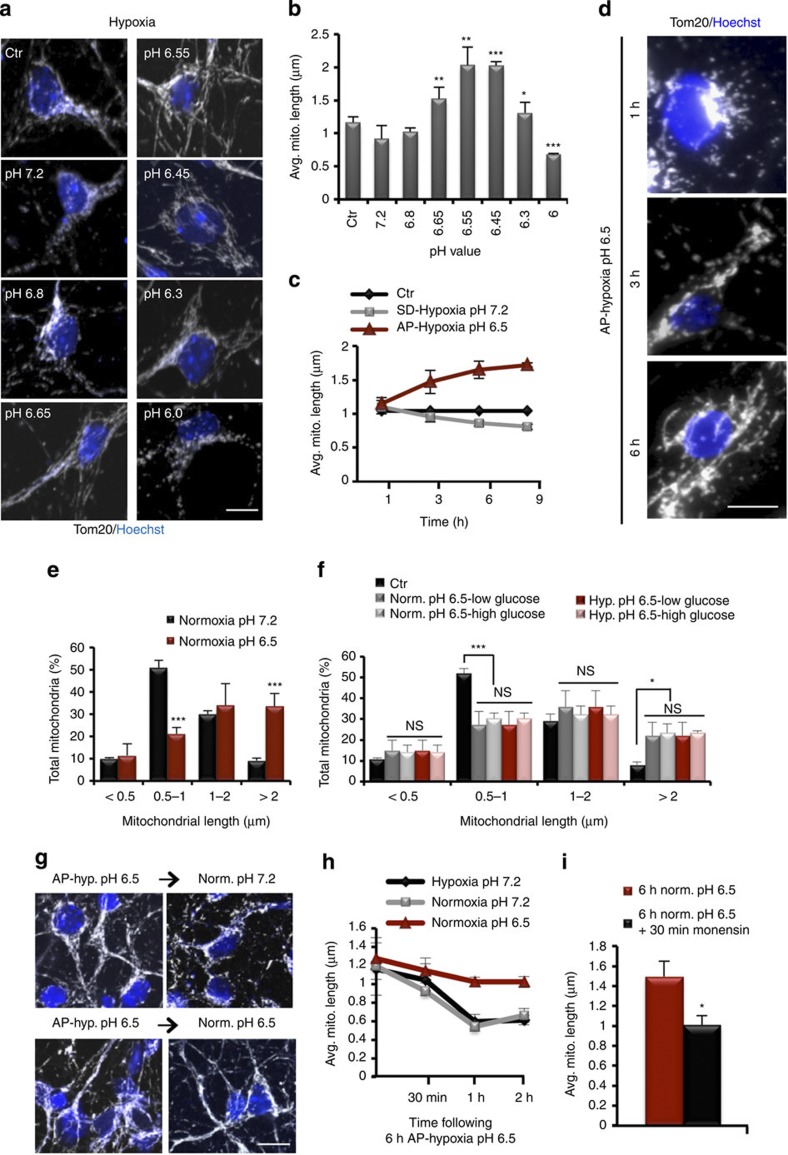
Figure 2. Acidosis-mediated mitochondrial elongation is pH-specific, rapid, reversible and O2- and glucose-independent.
(a) Representative confocal images of mitochondrial morphology in cultured cortical neurons following incubation at fixed pH values in hypoxia. Ctr=control; represents neurons incubated in neurobasal media. (b) Average mitochondrial length and s.d. (n=3) were plotted for the indicated pH values. (c) Average mitochondrial length and s.d. (n=3) over time at indicated conditions. (d) Immunofluorescence of Tom20 (mitochondria) showing the change in mitochondrial length in cortical neurons by physiological acidosis at the indicated times. (e) Mean and s.d. (n=3) of mitochondrial length distribution during normoxic conditions at indicated pH values for 6 h. (f) Mean and s.d. (n=3) of mitochondrial length distribution during normoxic or hypoxic conditions in the presence of low (5.5 mM) or high (25 mM) glucose levels for 6 h. (g and h) Analysis of mitochondrial morphology after 6-h incubation in AP-Hypoxia pH 6.5 and following reoxygenation at the indicated pH values. (h) Graph of the change in average mitochondrial length (s.d., n=3) at the indicated conditions following a 6-h incubation in AP-Hypoxia pH 6.5. (i) Average mitochondrial length and s.d. (n=3) were plotted for the indicated conditions. ns=not significant, *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (Student’s t-test). For all images scale=10 μm.