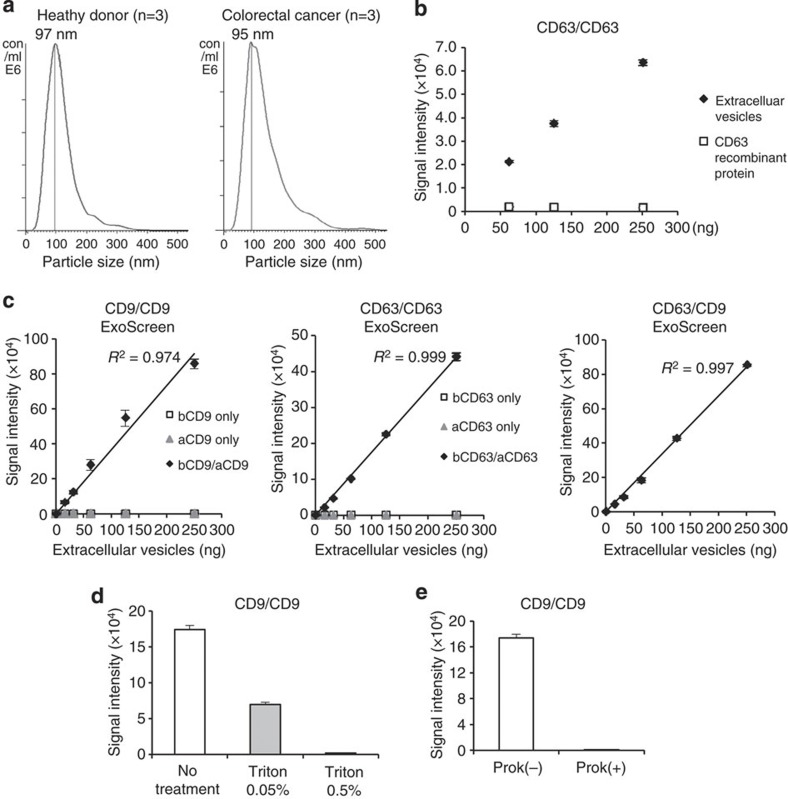
Figure 2. Establishment of ExoScreen to detect the EVs.
(a) Analysis of the size distribution in the serum of healthy donors (n=3) and colorectal cancer patients (n=3) by the NanoSight nanoparticle tracking system. (b) Detection of EVs or monomeric recombinant CD63 protein by ExoScreen using a CD63 antibody. EV protein concentration was measured via the Qubit system. The concentration of recombinant CD63 was adjusted with that of protein in EVs purified from HCT116 CM. Error bars are s.e.m. (n=3 for each condition). (c) Correlation between ExoScreen measurements for CD9 positive EVs, CD63 positive EVs or CD63/CD9 double-positive EVs and EV protein concentration in a dilution series. EV protein concentration was measured via the Qubit system. EVs were purified from HCT116 cell CM. The addition of biotinylated CD9 or CD63 antibodies without acceptor beads conjugated to antibodies is denoted ‘bCD9 only’ or ‘bCD63 only’, while ‘aCD9 only’ or ‘aCD63 only’ means addition of only acceptor beads conjugated to CD9 or CD63 antibodies without biotinylated antibodies. The addition of biotinylated antibodies and acceptor beads conjugated antibodies is denoted ‘bCD9/aCD9’ or ‘bCD63/aCD63’. Right panel shows the addition of biotinylated CD63 antibodies and acceptor beads conjugated CD9 antibodies. Error bars are s.e.m. (n=3 for each condition). (d) Evaluation of ExoScreen specificity against purified EVs from HCT116 cell treated with or without 0.05% and 0.5% Triton X-100. Two hundred fifty ng of EVs were detected by ExoScreen using CD9 antibodies. Error bars are s.e.m. (n=3 for each condition). (e) Evaluation of ExoScreen specificity against EVs from HCT116 cells treated with (Prok(+)) or without (Prok(−)) Proteinase K. Two hundred fifty ng of EVs were detected by ExoScreen using CD9 antibodies. Error bars are s.e.m. (n=3 for each condition). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments each.