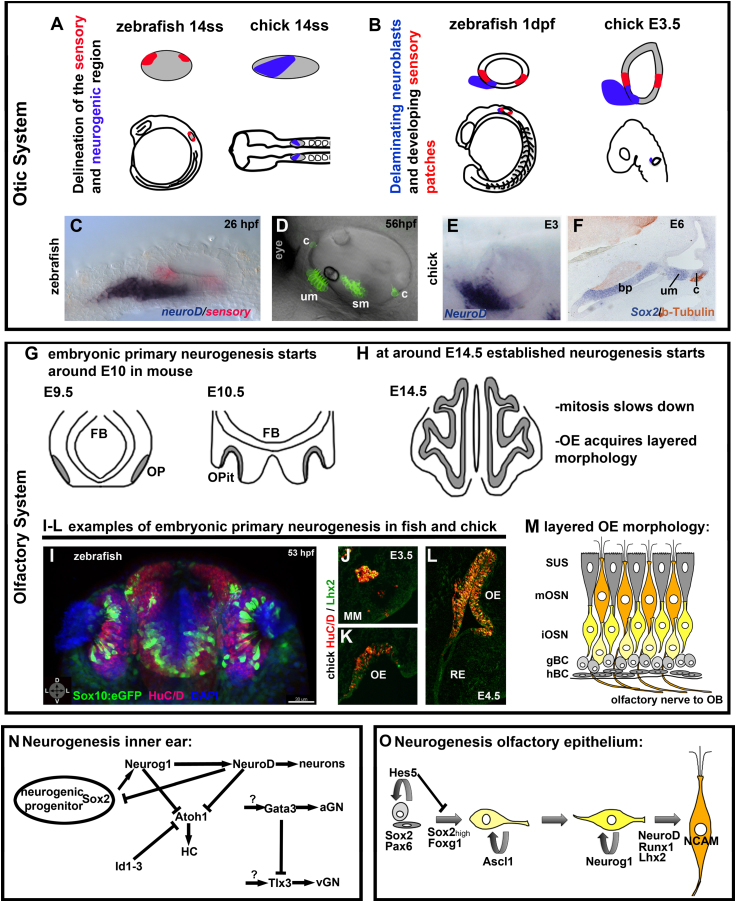
Fig. 2.
(A) Schematic drawing comparing the prospective neurogenic region in the otic placode from a 14 somite stage (ss) zebrafish embryo and a 14ss chick embryo. In the zebrafish, the sensory marker atoh1b is already expressed at 14ss (Millimaki et al., 2007), slightly ahead of the neurogenic marker neurog1 at 16ss (Radosevic et al., 2011). By contrast, in the chick, expression of ngn1 appears before the expression of sensory markers. (B) Schematic drawing depicting the delaminating neuroblasts and the developing sensory patches in the otic vesicle at comparable developmental stages in zebrafish and chick. (C) In situ hybridization showing neuroblasts (neuroD, blue) and sensory patches (red; unpublished sensory marker) in a 26 hours post fertilization (hpf) zebrafish otic vesicle. Lateral view; anterior to left. (D) Confocal z-stack projection of a Tg(pou4f3:GFP) zebrafish otic vesicle marking hair cells in the developing sensory patches at 56 hpf. Lateral view; anterior to top left, dorsal to top right. (E) In situ hybridization showing neuroblasts (neuroD, blue) in an E3 chick otic vesicle. Coronal section; anterior to the left, dorsal up. (F) In situ hybridization (Sox2, blue, marking sensory epithelia) and immunohistochemistry (β-Tubulin, brown, marking neuronal structures) in an E6 chick otic vesicle. Transverse section; medial to the left, dorsal up. (G) Schematic drawing depicting stages of olfactory placode development and primary neurogenesis in the mouse (coronal section). (H) Schematic drawing depicting the developmental stage that marks the transition from primary to established neurogenesis in mouse. (I) Example of primary neurogenesis in the zebrafish olfactory system. Confocal z-stack of antibody staining at 53 hpf: Tg(–4.9sox10:eGFP) (Wada et al., 2005; Carney et al., 2006) labels neural crest-derived microvillous neurons (Saxena et al., 2013), green; HuC/D labels post-mitotic neurons, red; nuclear stain, blue. Orientation arrows: D: dorsal; V: ventral; and L: lateral. Scale bar: 30 μm. (J–L) Examples of primary neurogenesis in the chick olfactory system. HuC/D labels post-mitotic neurons, red; Lhx2 labels progenitor cells and differentiated OSNs, green. (M) Schematic drawing depicting the layered morphology of the olfactory epithelium during established neurogenesis stages. (N) Scheme depicting the genetic network controlling neurogenesis in the inner ear. (O) Scheme depicting neurogenesis in the olfactory epithelium. Abbreviations: aGN: auditory ganglion neuron, bp: basilar papilla, c: crista, d: dorsal, dpf: days post fertilization, FB: forebrain, gBC: globose basal cell, HC: hair cell, hBC: horizontal basal cell, hpf: hours post fertilization, iOSN: immature olfactory sensory neuron, l: lateral, MM: migratory mass, mOSN: mature olfactory sensory neuron, OB: olfactory bulb, OE: olfactory epithelium, OP: olfactory placode, OPit: olfactory pit, RE: respiratory epithelium, sm: saccular macula, ss: somite stage; SUS: sustentacular cells, um: utricular macula, v: ventral, and vGN: vestibular ganglion neuron.