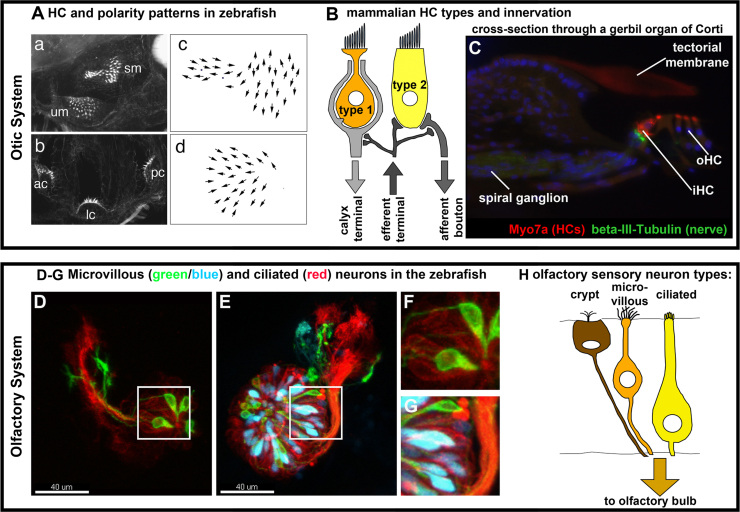
Fig. 3.
(A) Phalloidin stain and hair cell polarity patterns in zebrafish otic sensory patches at 3–4 days post fertilization: (a) utricular and saccular maculae, (b) cristae, (c) polarity pattern of the saccular macula and (d) polarity pattern of the utricular macula. Anterior to the left in all panels. Arrows in (c) and (d) are drawn from the stereociliary bundle to the kinocilium. Reproduced, with permission, from Hammond and Whitfield (2011). (B) Schematic drawing of the two types of mammalian vestibular hair cells and their innervation patterns. (C) Cross section through a gerbil organ of Corti. Myo7A labels hair cells, red; βIII Tubulin labels the spiral ganglion and nerve fibers, green; nuclei are labeled in blue. (D–G) Examples of olfactory cell types in live zebrafish at 29 hpf (D, F) and 60 hpf (E,G). Panels F and G show enlargements of the regions boxed in D and E, respectively. Confocal z-stacks of live embryos: Tg(TRPC24.5k:gap-Venus)/rw037 (Sato et al., 2005) labels all microvillous neurons, green; Tg(OMP2k:lyn-mRFP)/rw035 (Sato et al., 2005) labels all ciliated neurons, red; Tg(–4.9sox10:eGFP) (Wada et al., 2005; Carney et al., 2006) labels neural crest-derived microvillous neurons (Saxena et al., 2013), blue. Scale bar: 40 μm. (H) Scheme depicting sensory cells in the nasal epithelium. Abbreviations: ac: anterior crista, HC: hair cell, iHC: inner hair cell, lc: lateral crista, oHC: outer hair cell, pc: posterior crista, sm: saccular macula, and um: utricular macula.