Figure 2.
Premature Activation of Yen1 Causes Increased DNA Damage Sensitivity and Loss of Heterozygosity
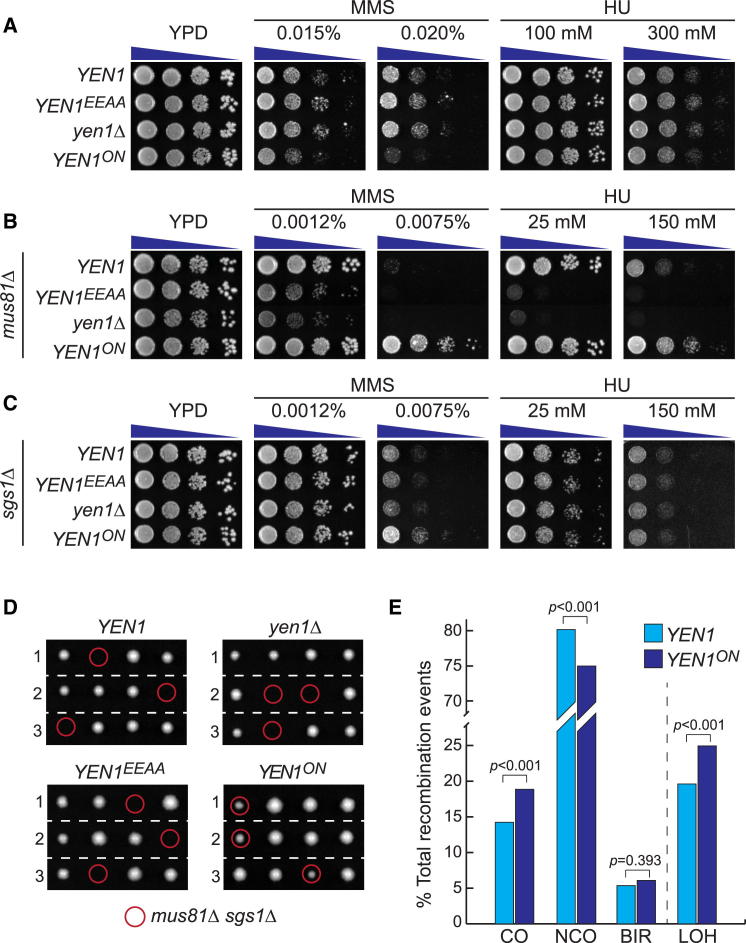
(A) Expression of Yen1ON at physiological levels causes MMS sensitivity. Assays were carried out as described in Figure 1C, using strains in which endogenous YEN1 was replaced by the indicated YEN1 alleles. Cells were plated on YPD containing the indicated amount of drugs.
(B) YEN1ON suppresses the DNA damage sensitivity of mus81Δ mutants. As in (A), but employing strains deleted for MUS81.
(C) Mild suppression of the MMS sensitivity of sgs1Δ mutants by YEN1ON.
(D) YEN1ON suppresses the synthetic lethality of mus81Δ sgs1Δ double mutants. Diploid strains homozygous for the indicated YEN1 alleles and heterozygous for MUS81/mus81Δ and sgs1Δ/SGS1 were sporulated and analyzed by tetrad dissection. Images were taken after 3 days incubation at 30°C. The expected position of each mus81Δ sgs1Δ colony is indicated (red circles).
(E) YEN1ON promotes crossover formation and loss of heterozygosity during mitotic recombination. The percentage of different recombination events in YEN1 and YEN1ON strains is indicated. CO, crossovers; NCO, noncrossovers; BIR, break-induced replication. LOH indicates the total loss of heterozygosity (the sum of CO and BIR events). p values were calculated using a chi-square test with Pearson’s correction.
See also Table S1.