Fig. 1.
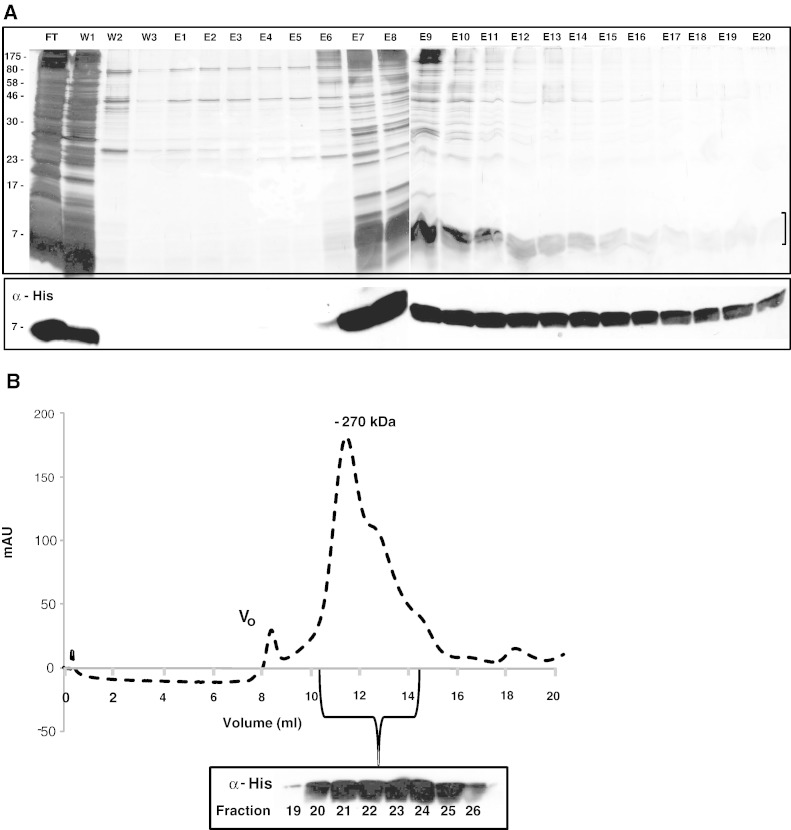
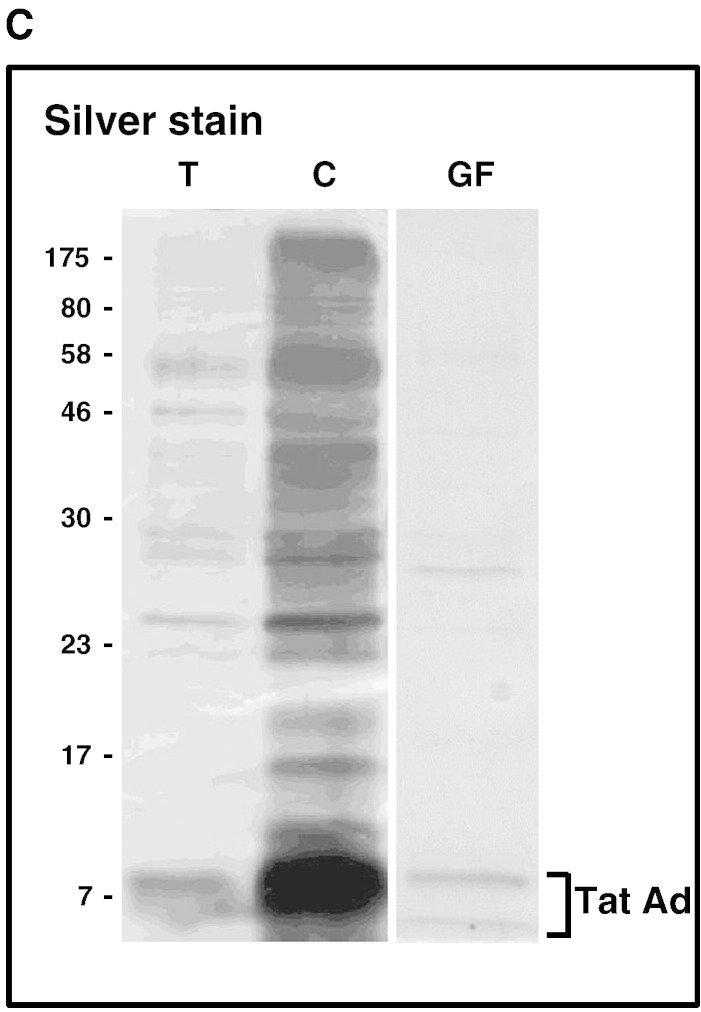
Purification of B. subtilis TatAd. (A) Membranes were isolated from E. coli Δtat cells expressing B. subtilis TatAd with a C-terminal His-tag, solubilised in DDM and applied to a Talon affinity column. The proteins in all elution fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE and the gels were analysed using silver staining or immunoblotting with antibodies against the His-tag. Talon column fractions: FT = flow-through, W1-3 = wash fractions, E1-E20 = elution fractions. The bracket indicates the position of TatAd which runs as a diffuse band. (B). A sample of the TatAd concentrate was applied to a Superdex 200 GL 30/100 gel filtration column. The run (240 μl sample, 0.5 ml/min flow, 0.02% DDM in buffer) shows a major peak at ~ 270 kDa with a shoulder towards lower molecular weights. The corresponding Western blot shows that TatAd elutes across fractions 19–26. Vo = void volume. (C) Silver-stained gel of elution fractions which contain TatAd for different stages in column purification. T = pooled Talon column elution fractions, C = pooled Talon fractions after concentration, GF = gel filtration elution fraction selected for electron microscopy studies. Positions of TatAd are indicated on the right of the figure and molecular weight markers are shown on the left.