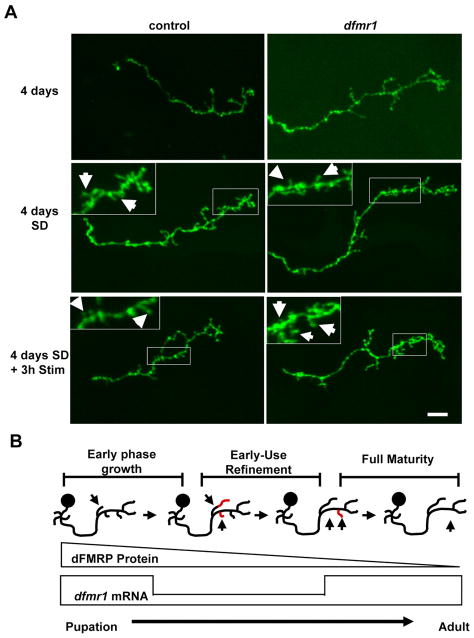
Figure 8. Sensory-deprivation modifies dFMRP-dependent axon pruning.
A) Representative images of single cell MARCM gamma neuron axon projections at 4 days post-eclosion. Animals raised in standard conditions (top row), sensory-deprived (middle row) and following 3 hours of normal sensory stimulation (bottom row). Scale bar=10μm. B) Diagram of dFMRP-dependent changes in MB axonal projections. dFMRP protein and mRNA are expressed maximally during late pupal development and the early-use period of the newly-eclosed animal. Activity-dependent pruning in MB axons occurs during this window, dependent on dFMRP. At maturity, transcriptional and translational regulation of dfmr1 becomes uncoupled as mRNA levels inversely correlate with protein levels.