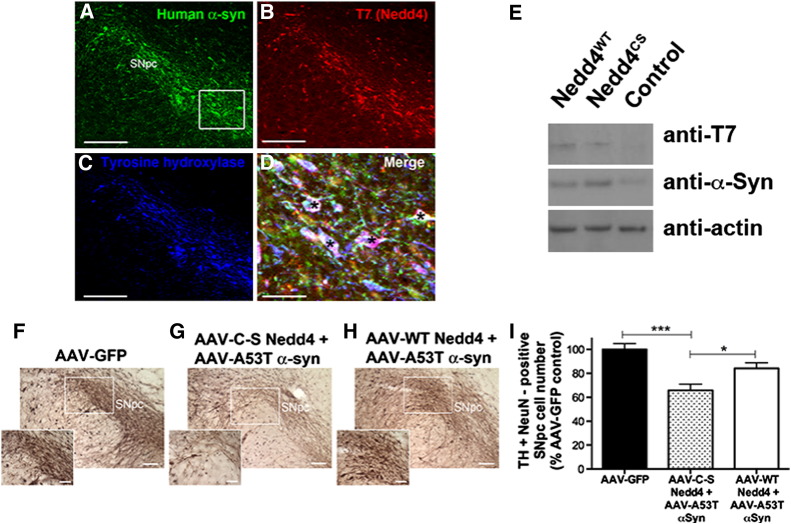
Fig. 4.
Overexpression of wild-type but not catalytically inactive Nedd4 prevents α-synuclein-induced loss of dopaminergic neurons. Virally-mediated overexpression of human A53T α-synuclein at 19 weeks post-AAV injection was confirmed using the LB509 antibody (panel A), and Nedd4 overexpression was verified using anti-T7 (panel B). TH was used to label dopaminergic neurons (panel C). Co-expression of both Nedd4 and human α-synuclein within TH-immunoreactive SNc neurons is shown in panel D, and represents the boxed area illustrated in panel A. Examples of TH-immunoreactive neurons expressing both transgenes are marked with asterisks. Expression was also confirmed by immunoblotting of SN lysates at 19 weeks with antibodies against α-synuclein (Syn1) and T7 for Nedd4 (panel E). Representative images and high magnification insets are shown in panels F–H for TH/NeuN doubly labeled neurons in the SNc for each group. (I) When compared to AAV-GFP controls (n = 5), there was a significant reduction in the number of dopaminergic neurons in rats expressing Nedd4C-S and A53T α-synuclein (n = 8) whereas co-expression of Nedd4WT (n = 7) afforded protection. *p < 0.05, p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA, Tukey's multiple comparison post-hoc test). Scale bar, panels A, B = 200 μm, panel D = 50 μm, panels F–G = 100 μm, insets = 50 μm.