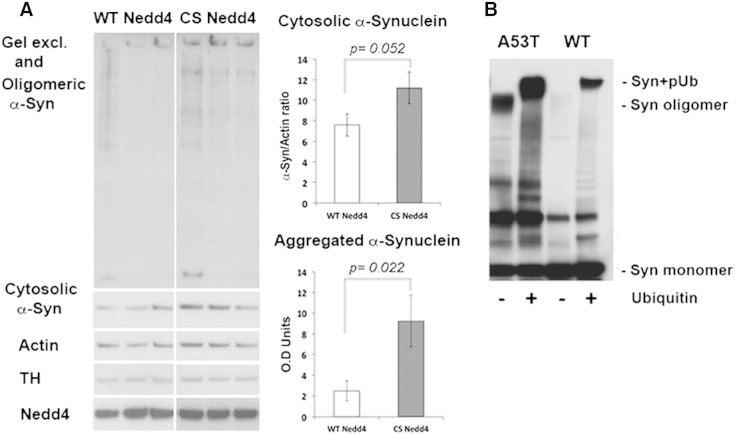
Fig. 5.
Wild-type but not catalytically inactive Nedd4 prevents α-synuclein accumulation in the rat SN. The level of cytosolic and aggregated α-synuclein was quantified following serial fractionation and immunoblotting of SN lysates at 19 weeks post-AAV injection of either A53T α-synuclein/Nedd4WT or A53T α-synuclein/Nedd4C-S. (A) Representative immunoblot showing cytosolic and aggregated α-synuclein at 19 weeks post-AAV injection for three animals per group. Actin is shown as loading control. Quantitative band densitometry (n = 5–6 animals per group) showed that the cytosolic α-synuclein content was reduced by 33% in rats co-expressing Nedd4WT (panel A, upper histogram) whereas the RIPA-insoluble/SDS soluble (gel excluded and oligomeric) α-synuclein, was significantly increased by 3.6-fold in rats co-expressing Nedd4C-S (panel A, lower histogram). B. Recombinant wild-type and A53T mutant α-synuclein was incubated with purified Nedd4, UbcH5 as the E2 with or without ubiquitin, and ubiquitination was assayed using anti-α-synuclein antibodies. Polyubiquitination (syn + pUb) of both recombinant WT and A53T mutant α-synuclein by Nedd4 was detected. High molecular weight species of aggregated A53T α-synuclein, present in the reaction before ubiquitin was added, were also ubiquitinated by Nedd4 as evidenced by the increase in their molecular weight upon addition of recombinant ubiquitin. Monomeric α-synuclein was added in excess and thus not clearly depleted in this reaction.