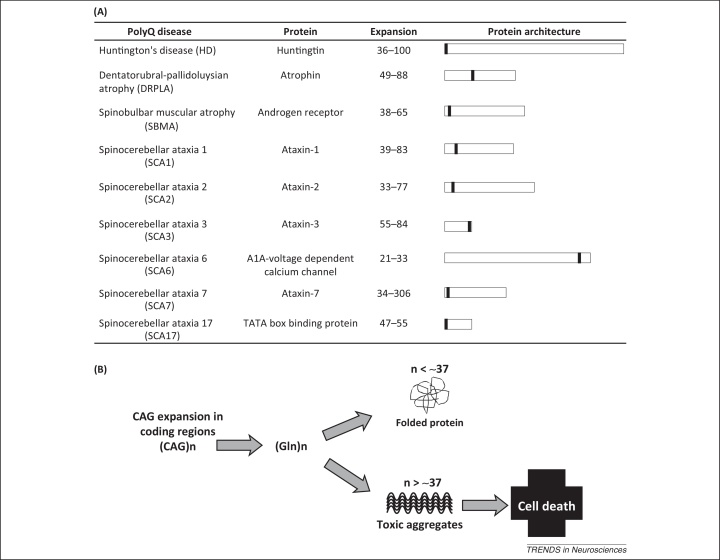
Figure 1.
Expansion of a polyglutamine (polyQ) tract in specific proteins is associated with neurodegeneration. (A) A list of the currently known polyQ diseases with protein name, pathological threshold, and protein architecture. The position of polyQ in the sequence is indicated as a black rectangle on the protein schematic representation. (B) Schematic representation of the disease mechanism. When the repeat number is lower than a threshold (∼37 repeats), the proteins are correctly folded and functional; when it is above the threshold, the carrier proteins aggregate and misfold with consequent cell toxicity and death.