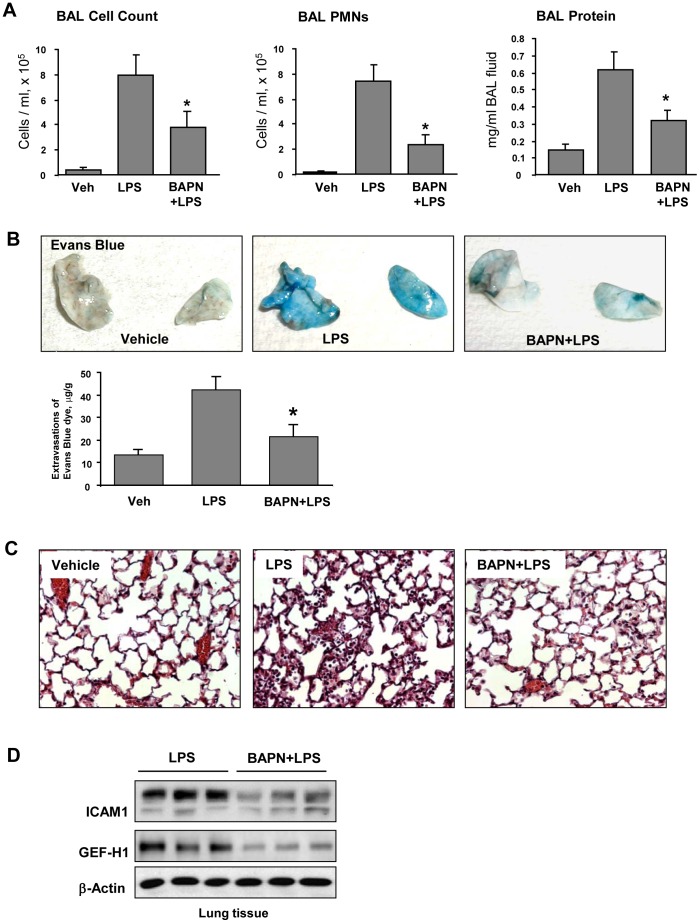
Figure 7. Effect of LOX inhibitor on LPS-induced lung inflammation and barrier dysfunction.
C57BL/6J mice were challenged with vehicle or LPS (0.63 mg/kg, i/t) with or without BAPN treatment (100 mg/kg). Control animals were treated with sterile saline solution. A – Total cell count, PMN cell count and protein concentration were determined in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid collected 48 hrs after treatments. B - Evans blue dye (30 ml/kg, i/v) was injected 2 hr before termination of the experiment. Lung vascular permeability was assessed by Evans blue accumulation in the lung tissue. The quantitative analysis of Evans blue labeled albumin extravasation was performed by spectrophotometric analysis of Evans blue extracted from the lung tissue samples; *p<0.05. C – Histological analysis of lung tissue by hematoxilin & eosin staining (×40 magnification); D - Expression of ICAM-1 and GEF-H1 in lung tissue samples evaluated by western blot analysis. Equal protein loading was confirmed by membrane re-probing with β-actin antibody.