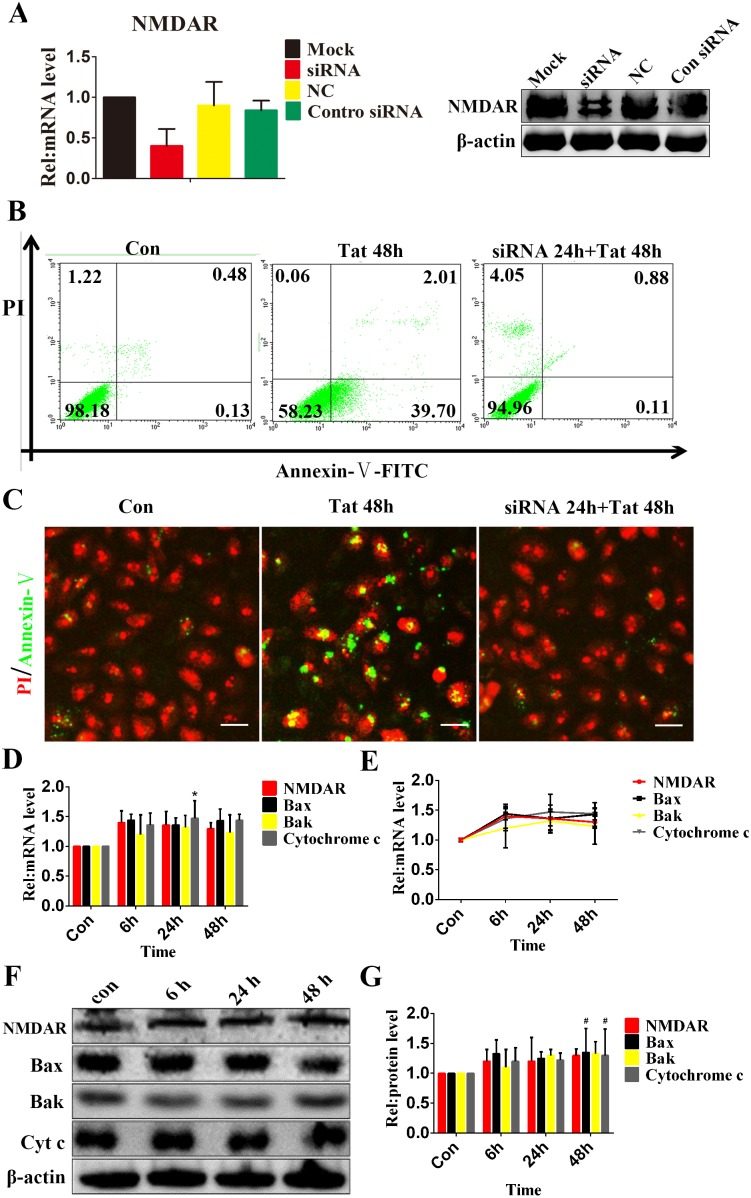
Figure 5. Silencing of NMDARs inhibits Tat-induced RPE apoptosis.
ARPE-19 cells were transfected with NMDAR1-specific small interfering RNA for 24 hours, and the degree of NMDAR1 silencing was estimated using qPCR and Western blotting (A). Representative flow cytometry images show early apoptotic cells in which NMDAR was knocked down for 24 h, Tat was added, and incubation continued for an additional 48 h. Apoptotic cells were visualized using Annexin V-FITC staining (B). Immunofluorescence micrographs showing apoptotic cells using Annexin V-FITC staining (green); the nuclei were counterstained with PI (red). Scale bar: 50 µm. Both of these analyses showed that the knockdown of NMDAR could protect RPE cells from the apoptosis induced by Tat (C). After the silencing of NMDAR1 for 24 h, ARPE-19 cells were cultured with Tat for 0, 6, 24 or 48 h. The expression levels of NMDAR1, Bax, Bak and Cytochrome c were quantitated using qPCR (*, P<0.05 vs. control) (D) (E) and Western blotting (F). The corresponding graphs show the quantification of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate; the data were normalized to cells without Tat treatment (#, P<0.05 vs. control) (G).