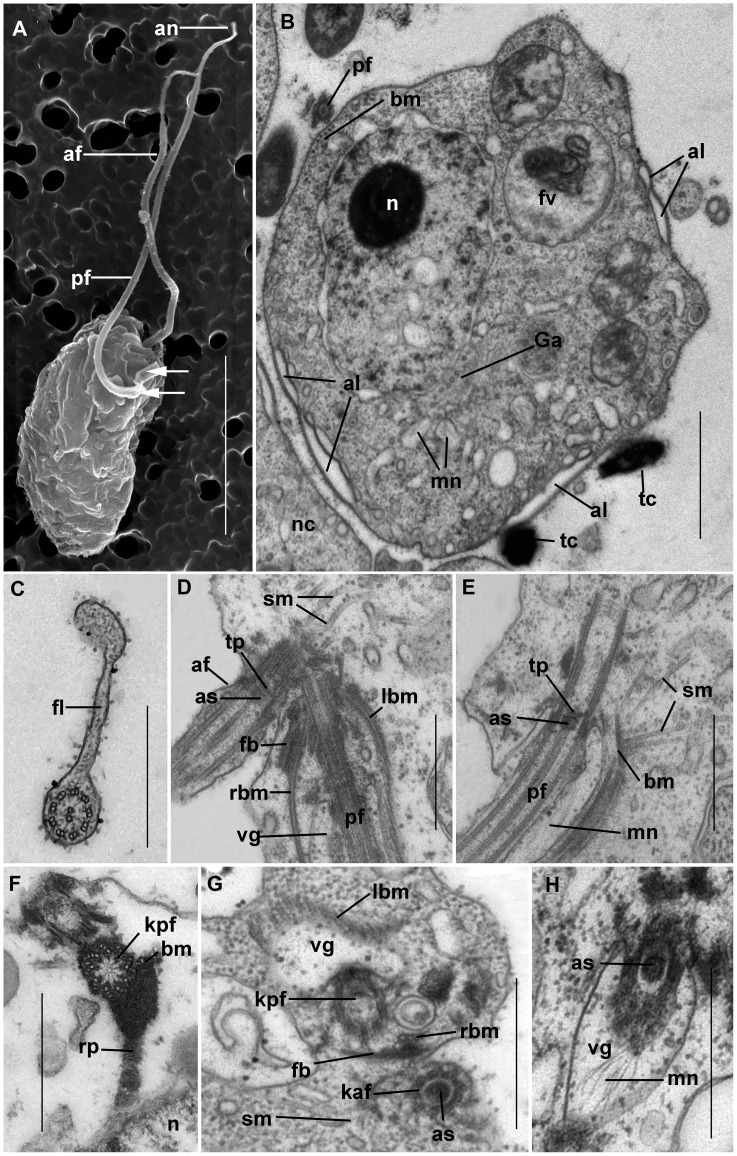
Figure 4. Ultrastructure of Colponema vietnamica.
a) Electron micrograph of the cell. Anterior and posterior flagella (af and pf) end with narrowing tips – acronemes (an). The arrows point to the short fold of proximal part of the pf. b) The transversal section at the level of the nucleus (n). In some places the cell contains the alveoli (al) beneath the plasmalemma. Small cytosolic vesicles contain the rudiments of the mastigonemes (mn). Golgi apparatus (Ga) is situated close to the nucleus. Discharged toxicysts (tc) are found outside of the cell. The band of 5+1 microbules (bm) accompanies the pf. Food vacuole (fv) contains remnants of a prey cell. The neighboring cell (nc) is seen. c) The cross section of the pf. The thin fold (fl) is visible. d) Flagella are arranged mutually at an angle of 45 degrees. Right and left bands of microtubules (rbm and lbm) and fibrous band (fb) emerge from the bases of the pf which runs inside the short ventral groove (vg). The secondary microtubules (sm) run near af. The axosoma (as) is visible above the transverse plate (tp). e) The pf inside vg. sm originate from the microtubular band (bm). The conspicuous as is located above the transverse plate (tp) of the flagellum. Mastigonemes (mn) cover the pf. f) The short amorphous rhizoplast (rp) extends from the kinetosome of the posterior flagellum (kpf) towards the nucleus (n). G. Kinetosome area. Three microtubules (rbm) and fibrous bands (fb) lie close to the kpf. vg is armored by the left band of microtubules (lbm). Kinetosome of anterior flagellum (kaf) contains an axosome (as). Single secondary microtubules (sm) are seen. h) pf passes in the vg and bears thin mastigonemes (mn). as is visible in the transitional zone of the flagellum. Scales: 0.5 µm in (c–h); 1 µm in b); 5 µm in a).