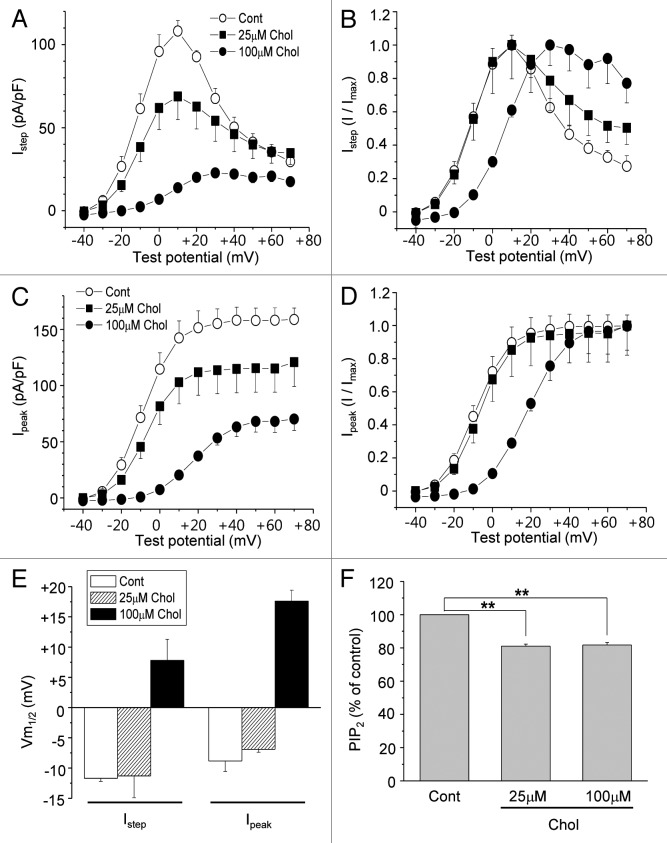
Figure 2. Mild augmentation of membrane cholesterol levels inhibits HERG K+ currents without changing the voltage dependence curve. (A and C) Averaged current-voltage relations obtained for HERG K+ currents (n = 7). Cells were incubated with 25 μM or 100 μM MβCD-cholesterol for 1–2 h at 37 °C before recordings. Currents were measured at the end of the depolarizing step (A; Istep) or peak tail current amplitude (C; I peak) following the step to −40 mV as described in Figure 1C. (B and D) The voltage-dependent activation curves for Istep and Ipeak were obtained by normalizing the data at (A) and (C), respectively. (E) Voltage-dependent activation curves at (B) and (D) were fit with Boltzmann equations, and the resulting half voltages to maximal activation (Vm1/2) were compared. (F) PtdIns(4,5)P2 levels in the membrane fractions were measured by using PtdIns(4,5)P2 ELISA kit as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were treated with 25 μM or 100 μM MβCD-cholesterol for 1 h at 37 °C. **p < 0.01

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.