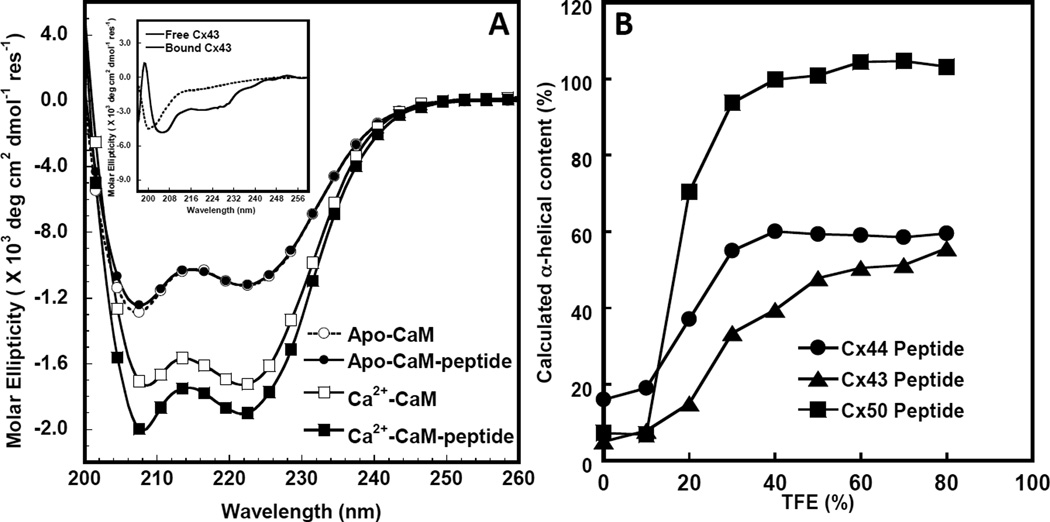
Figure 3. Circular dichroism studies of the interaction between Cx43p136–158 and Apo/Holo CaM.
A. Far UV circular dichroism spectrum of CaM in the presence of 1 mM EGTA (white circle) or 1 mM CaCl2 (white square) and a 1:1 CaM/synthetic peptide mixture with 1 mM EGTA (black circle) or 1 mM CaCl2 (black square) after subtracting the contribution from the buffer. Buffer conditions: 10 mM Tris, 100 mM KCl at pH=7.4 at room temperature. The insetdemonstratesthe far UVcircular dichroism spectra of Cx43p136–158 (dashed line) and the calculated difference spectrum (solid line) by subtracting the spectrum of Ca2+-CaM from that of the Ca2+-CaM-Cx43p136–158 mixture with 1 mM Ca2+ in a buffer consisting of 100 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl, at pH=7.4. B. TFE induced α-helical content increase of Cx43 (triangle), Cx44 (circle) and Cx50 (square) peptides corresponding to CaM-binding sites.