Figure 5.
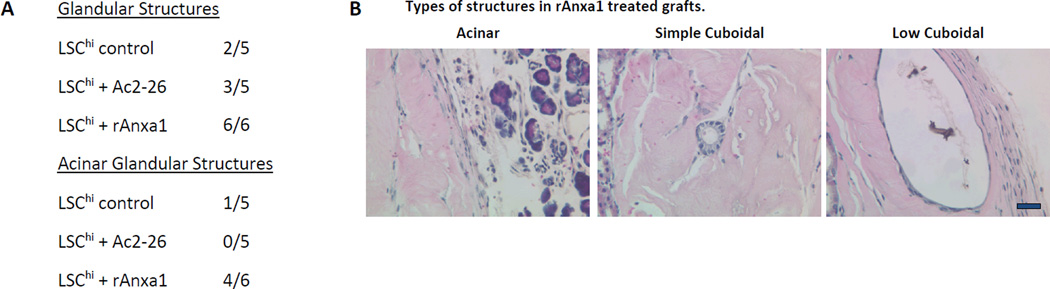
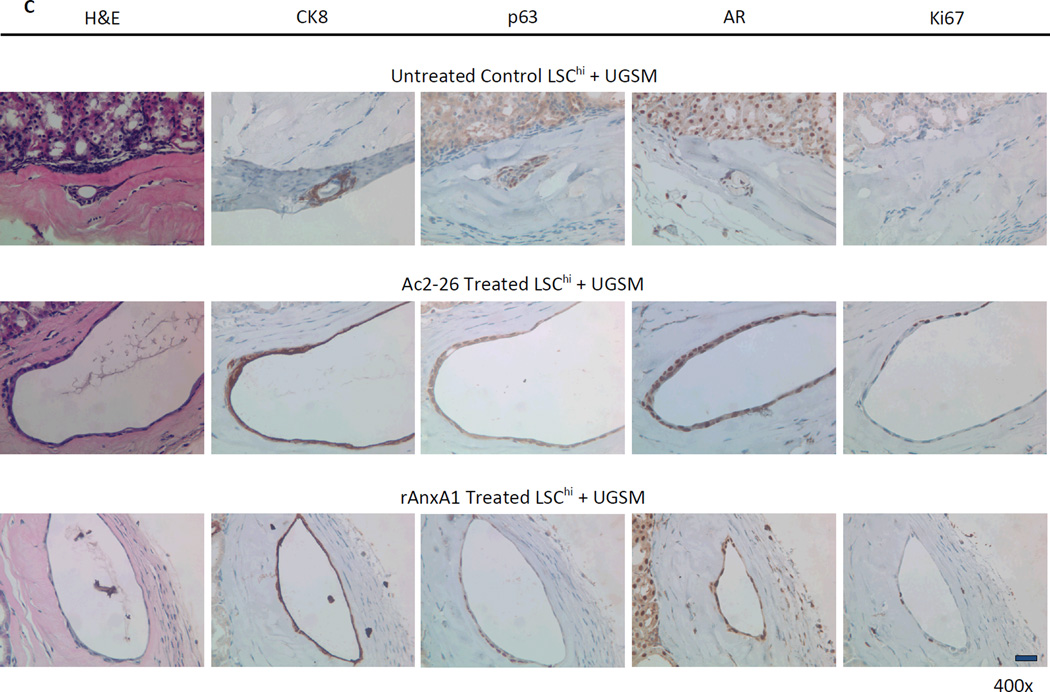
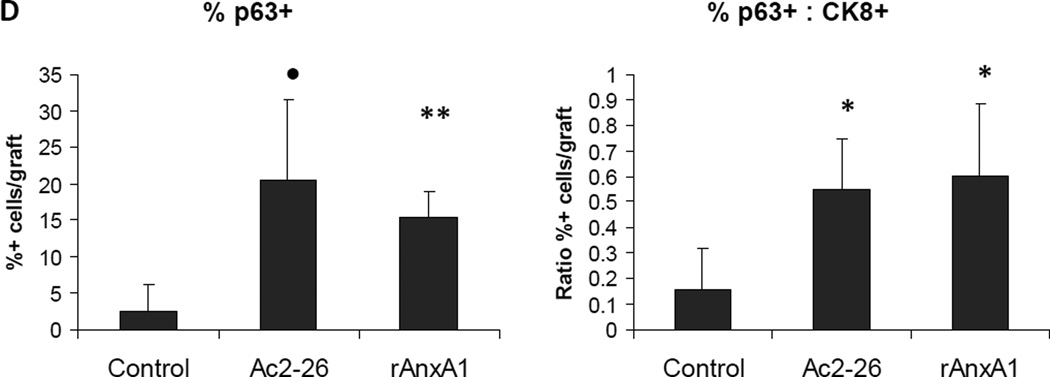
Effect of AnxA1 on incidence, types, differentiation and proliferation of glandular structures in LSChi grafts. A, Chart depicting the incidence and type of glandular structures (cuboidal or acinar type glandular) scored in LSChi untreated control, Ac2-26 treated and rAnxA1 treated grafts. B, Representative H&E images of the types of structures detected in rAnxA1 treated grafts. Magnification at 400×. Bar 100 µm. C, Tissue sections were analyzed by H&E for basic histology and IHC for expression of basal cell marker p63, luminal cell marker CK8, androgen receptor (AR) and Ki67. Magnification at 400×. Bar 100 µm. D, Calculated percentage of p63+ cells and ratio of p63+ to CK8+ cells detected in the grafts. Potential to undergo de-differentiation in response to AnxA1 was assessed by increase in p63 expression compared to CK8. Statistical significance is indicated by *, P < 0.05; •, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001.