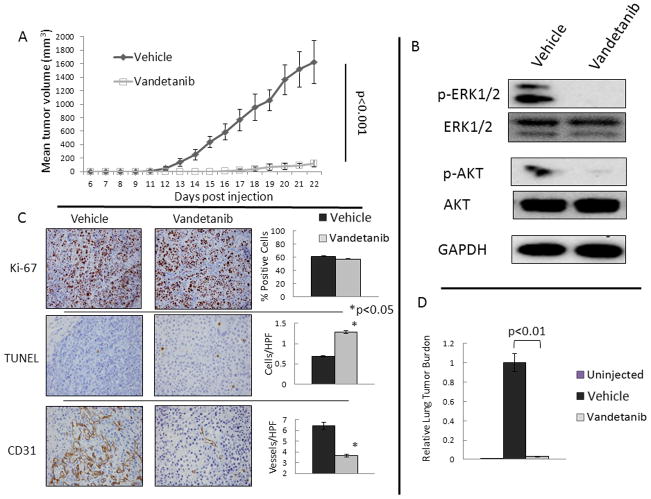
FIGURE 2. Vandetanib Inhibits MCF-7 Xenograft formation.
A. Ten mice were treated with vandetanib, 25 mg/kg daily by oral gavage from the time of tumor injection, and had reduced tumor formation and growth compared to ten vehicle gavaged animals. Mean tumor volume is shown with error bars representing the standard deviation. B. Protein from xenograft tumors demonstrates decreased activation of the RET pathway downstream targets ERK1/2 and AKT in vandetanib treated animals compared to control treated. Three tumors from each group were analyzed by western blot and representative blots are shown. C. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed on all 20 tumors with representative slides shown and quantified with graphs representing the mean and standard deviation of the spread of data for the treatment and vehicle groups. IHC of tumors demonstrates no change in proliferative index (Ki-67) with vandetanib treatment. Vandetanib caused a significant induction of apoptosis measured by TUNEL positive cells, and resulted in a reduction in microvessel density measured by CD31. Stars indicate p<0.05. D. Treatment with vandetanib reduces detectable tumor cells in the lung. The p values were calculated using the Student’s t-test for continuous variable data.