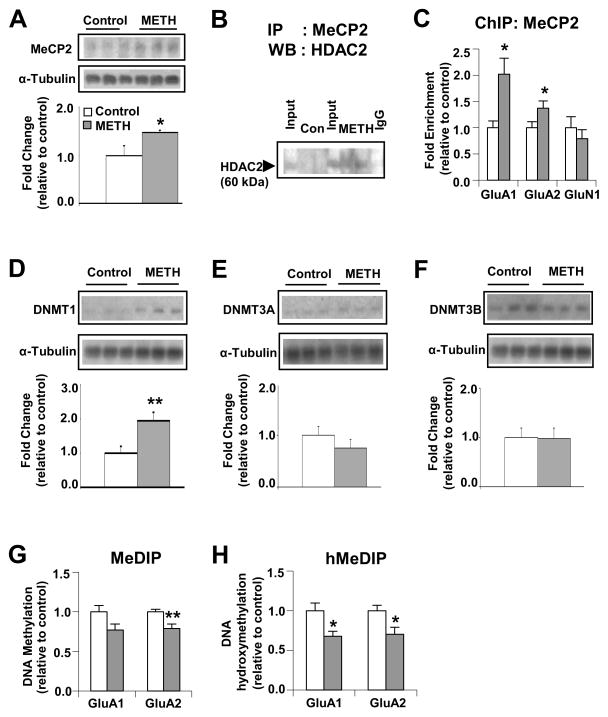
Figure 6.
Chronic METH exposure causes down-regulation of GluA1 and GluA2 transcription by formation of a MeCP2-HDAC2 complex. Western blot analysis of (A) MeCP2, (D) DNMT1, (E) DNMT3A and (F) DNMT3B Representative photomicrographs show results of 3 samples per group. For quantification, the signal intensity was normalized to 3-tubulin. Co-immunoprecipitation assays of (B) MeCP2 and HDAC2 show METH-induced interactions of MeCP2 with HDAC2. The level of HDAC2 from non-specific IgG is indicated. Input levels (5 %) of HDAC2 are shown for comparison. ChIP assays (n=6 – 8 rats per group) were carried out using antibodies against MeCP2 (C). Quantitative PCR was conducted using specific ChIP primers (see Table S2). Denatured genomic DNA of ~200 – 600 bp (generated by sonication) was incubated with an antibody directed against 5mC (G) or 5hmC (H), in order to isolate methylated or hydroxymethylated DNA by immunoprecipitation. Relative enrichment of 5mC and 5hmC in the bound over input fractions was calculated by real-time PCR. Values represent means ± SEM of fold enrichment relative to the controls. Statistical significance was determined by un-paired Student’s t-test. Key to statistics: * p< 0.05; ** p< 0.01; *** p< 0.001 vs. control group.