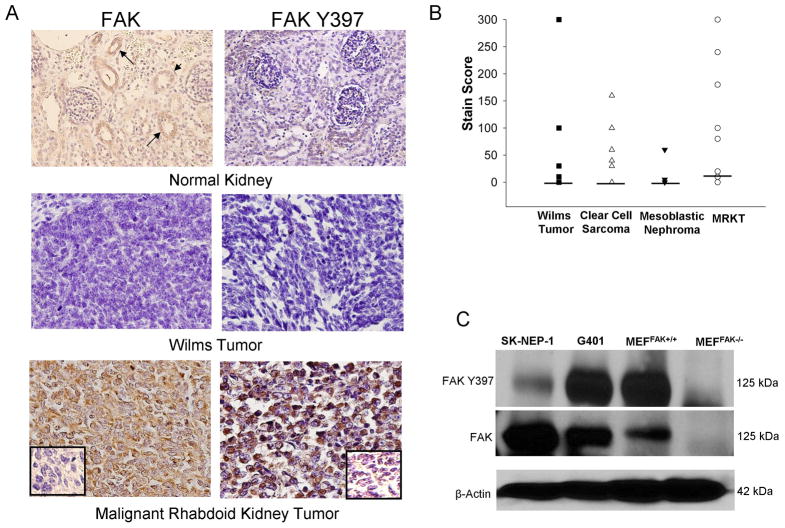
Figure 1.
FAK in pediatric renal tumor specimens and cell lines. A. Immunohistocemistry staining with antibodies specific for FAK and phospho-FAK was perfomed on 55 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human pediatric renal tumor specimens (12 malignant rhabdoid kidney tumor, 12 clear cell sarcoma, 19 Wilms tumor, and 12 mesoblastic nephroma). Representative photomicrographs presented show weak FAK staining in the eipthelium of the renal tubules (top left panel, closed arrows) but no FAK phosphorylation (top right panel) in normal human kidney. Staining for FAK and phospho-FAK was not present in the majority of Wilms tumor specimens (middle panels). Strong staining for FAK and phospho-FAK was noted in most of the malignant rhabdoid kidney tumor specimens (bottom panels). Negative controls were included with each run (inserts, bottom panels). B. Stain scores were calculated for the IHC specimens listed above and reported as the range and median (bar). All tumor types, except for the MRKT, had a median stain score of 0. The median stain score for the MRKT specimens was 15. C. Immunoblotting for Y397 FAK and total FAK was performed on SK-NEP-1 and G401 renal tumor cell lysates. FAK was detected in both of the renal tumor cell lines and was phosphorylated. Lysates from mouse endothelial fibroblasts with (MEFFAK+/+) and without (MEFFAK−/−) FAK served as controls.