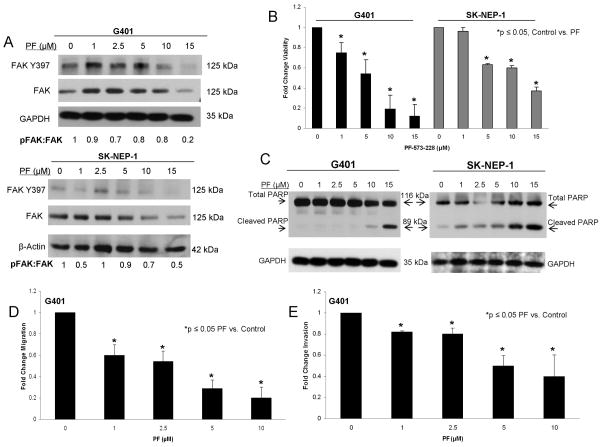
Figure 3.
PF-573,228 (PF) inhibition of FAK in human renal tumor cell lines. A. G401 and SK-NEP-1 cell lines were treated for 24 hours with increasing concentrations of PF-573,228 (PF). Cell lysates were harvested and evaluated with immunoblotting for total FAK and FAK Y397. Densitometry was performed, and FAK phosphorylation was reported as a ratio between the densities of the Y397 band to the total FAK band. Increasing concentrations of PF led to decreased FAK phosphorylation (Y397) in both cell lines. B. AlamarBlue® assays were used to assess cell survival. Both G401 and SK-NEP-1 cell lines showed significantly decreased cell survival following treatment with PF for 24 hours. C. Immunoblotting for cleaved PARP was utilized to detect apoptosis. G401 and SK-NEP-1 cells were treated with PF for 24 hours and cell lysates collected. Immunoblotting showed increased cleaved PARP following PF treatment in both cell lines, indicating apoptosis. D. G401 cells were treated with PF at increasing concentrations and allowed to migrate through a micropore insert. Migration was reported as fold change in the number of cells migrating through the membrane. Cellular migration was significantly diminished following treatment with PF. These effects were seen at a concentration of 1 μM PF. E. G401 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of PF and allowed to invade through a Matrigel™ coated micropore insert. Cells were counted and invasion reported as fold change. Invasion, similar to migration, was significantly decreased after exposure to 1 μM PF. All experiments were repeated at least in triplicate and data reported as mean fold change ± SEM.