Fig. 2.
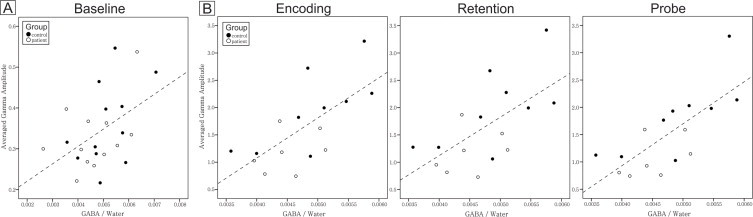
A. Relationship between gamma amplitude and GABA level in the resting state. The filled circles are controls and the open circles are patients. Across groups, the baseline gamma amplitude of the F3 electrode significantly correlated with the baseline GABA level of left DLPFC (two-tailed Pearson's correlation coefficient, N = 24, R = 0.48, P = 0.019). B. Relationships between averaged gamma amplitudes during all three stages (i.e., encoding, retention, and probe) of the working memory task and the baseline GABA level of the left DLPFC. Working memory EEG data consisted of nine controls and seven patients. For each participant, averaged gamma amplitude across trials was computed for each stage. For each working memory stage, two-tailed Pearson's correlation coefficient between baseline GABA and task-induced gamma amplitude was computed. Each stage exhibited a significant correlation between gamma amplitude and GABA level (two-tailed Pearson's correlation coefficients with Bonferroni correction for three stages: corrected alpha level = 0.05/3 = 0.017; n = 16; encoding stage, R = 0.68, P = 0.004; retention stage, R = 0.63, P = 0.009; probe stage, R = 0.73, P = 0.001). Furthermore, within each group and across stages, correlation coefficients are all positive. The correlation coefficients are stronger in healthy controls than in patients.
