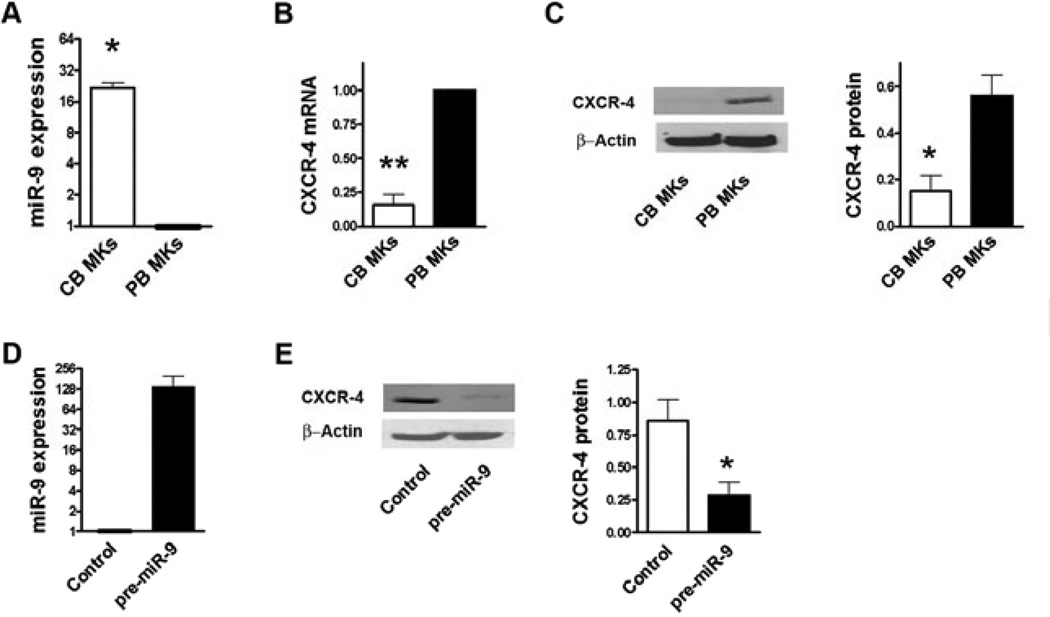
Figure 1. hsa-miR-9 regulates the expression of CXCR-4.
CXCR-4 and hsa-miR-9 levels were measured in human primary MKs derived from cord blood (CB) and from adult peripheral-blood (PB) CD34+ progenitors. (A) hsa-miR-9 values were normalized against U6 (internal control), and CB values were expressed as a ratio to adult PB values. hsa-miR-9 levels were significantly higher in CB-derived compared to adult PB-derived mature MKs. (B) CXCR-4 mRNA levels, expressed as a ratio to beta actin, were significantly lower in CB-derived compared to adult PB-derived MKs. (C) CXCR- 4 protein levels (ratio to beta actin) were significantly lower in CB-derived compared to adult PB-derived MKs. (D) To determine whether CXCR-4 is regulated by miR-9 in MKs, Meg-01 cells were nucleofected with either pre-miR-9 or a non-targeting scrambled oligonucleotide as control. hsa-miR-9 expression was 136.2±63.9 fold higher in cells nucleofected with pre-mir-9 than in cells nucleofected with the control oligo. (E) CXCR-4 protein expression was consistently down-modulated in cells over-expressing miR-9, as shown in this representative Western Blot and the bar graph summarizing the results of multiple experiments. Bar graphs represent the mean±SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. Mann-Whitney tests were used to compare the two groups. Statistical difference was defined as p<0.05 using SSPS15.0. *P<0.05. **P<0.01.