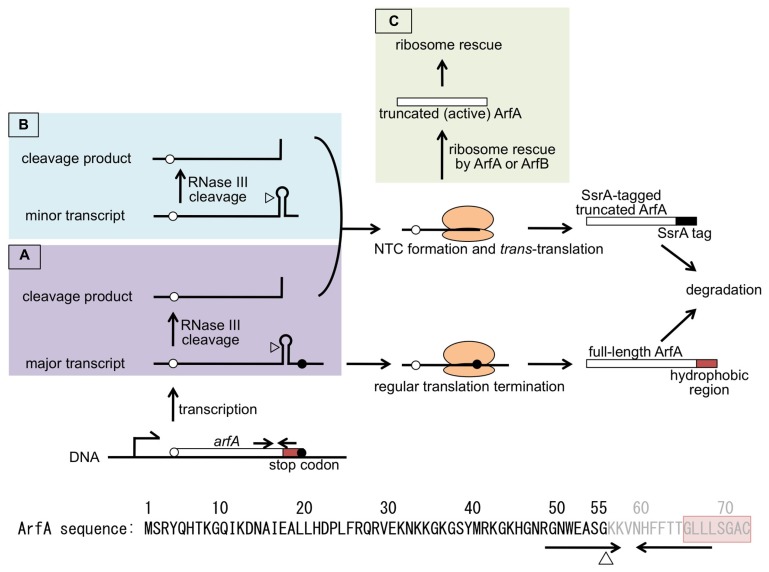
FIGURE 2.
Model for trans-translation-mediated regulation of ArfA expression. arfA is transcribed as mRNA with (A) or without (B) stop codon. In both cases, mRNA is cleaved by RNase III at the site indicated by triangle. This results in the non-stop mRNA formation. ArfA translated from arfA mRNA with stop codon (A, bottom) will be degraded due to its hydrophobic C-terminus (red box). Translation of arfA non-stop mRNAs (A, top; B) results in NTC formation. The NTC is normally resolved by trans-translation and translated ArfA will be degraded due to the SsrA-tag (closed box) attached to its C-terminus. Once the level of NTC exceeds the capacity of trans-translation, NTC will be resolved first by SsrA-tagged ArfA escaped from proteolysis or ArfB, then by truncated ArfA which is produced from non-stop mRNA (C). ArfA thus produced functions as a back-up ribosome rescue factor for trans-translation system. Amino acid sequence of ArfA is shown at the bottom. Positions corresponding to the inverted repeat (arrows) and RNase III cleavage site (triangle) are shown below the sequence. ArfA produced from the RNase III-processed arfA mRNA lacks its C-terminus portion which shown in gray characters.